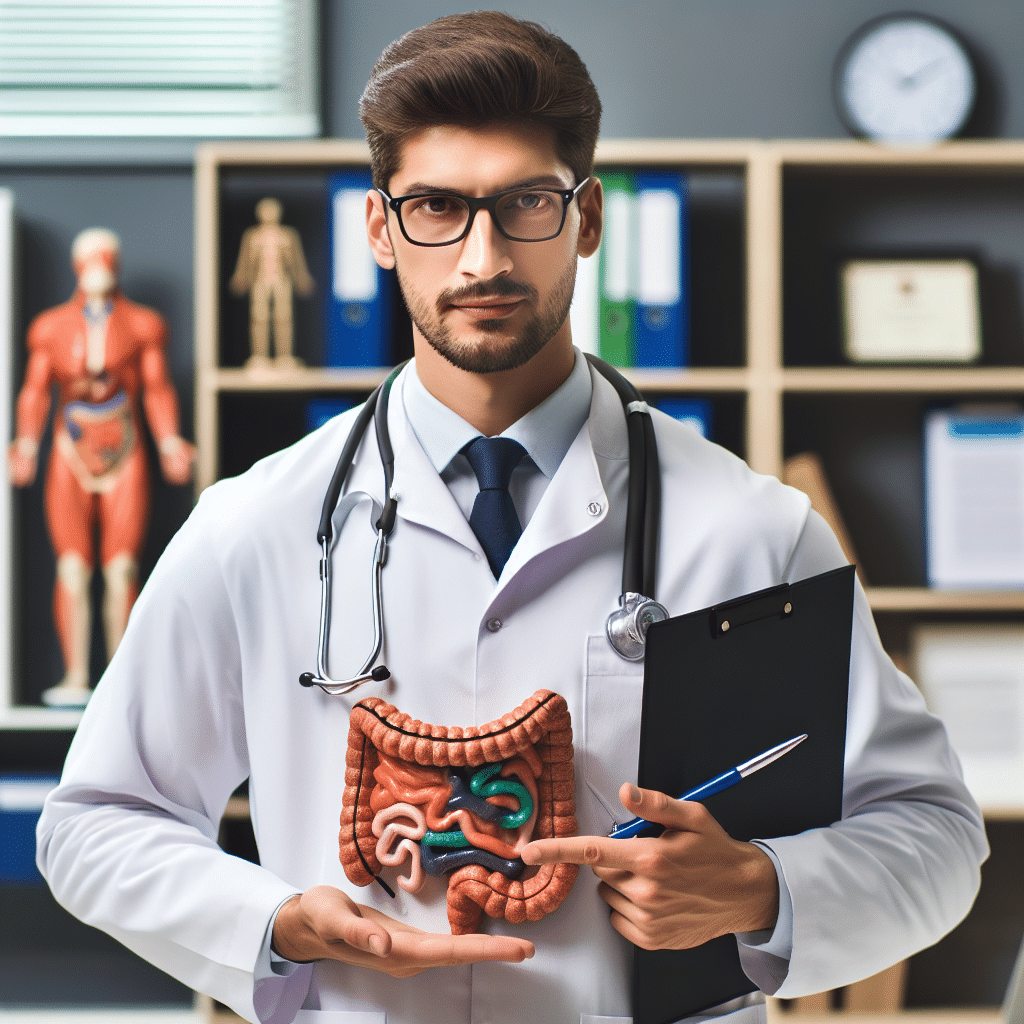
A GI doctor, or gastroenterologist, specializes in diagnosing and treating disorders of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, which includes the stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. They are experts in conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and liver diseases. GI doctors perform various diagnostic procedures, including endoscopies, to examine the lining of these organs and can provide treatments ranging from medication management to more complex interventions like surgery. Patients typically seek the expertise of a GI doctor when experiencing symptoms such as persistent abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, or severe gastrointestinal discomfort. Thus, a GI doctor plays a critical role in maintaining digestive health and treating complex conditions effectively.
Understanding the Role of a GI Doctor
Gastroenterology is a subspecialty of internal medicine that focuses on the study and treatment of the gastrointestinal tract and its associated organs. As a GI doctor, one is trained to understand the intricate functions of the digestive system, diagnose its disorders, and manage them through both pharmacological and non-pharmacological means. Their expertise is essential for maintaining overall health, as the gastrointestinal system is fundamental to the body’s ability to digest food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste.
Education and Training Required to Become a GI Doctor
To become a gastroenterologist, an individual must first complete a bachelor’s degree, followed by a medical degree from an accredited institution. Afterward, they undertake an internal medicine residency, usually lasting three years. Following residency, aspiring GI doctors must complete a gastroenterology fellowship, which typically spans an additional two to three years. This rigorous training includes practical experience in diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal illnesses, as well as performing diagnostic procedures such as colonoscopies and endoscopies.
Common Conditions Treated by GI Doctors
GI doctors have expertise in a broad range of gastrointestinal conditions, including:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): This includes conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, which involve chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): A chronic digestive condition where stomach acid or bile irritates the food pipe lining, causing symptoms like heartburn.
- Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver, which can be caused by viruses, excessive alcohol consumption, or autoimmune diseases.
- Celiac Disease: An autoimmune disorder that occurs in genetically predisposed individuals where ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine.
Diagnostic Procedures Performed by GI Doctors
GI doctors employ various diagnostic techniques to evaluate gastrointestinal disorders effectively. Some of the most common procedures include:
- Endoscopy: A procedure that allows the doctor to directly view the inside of the digestive tract using a flexible tube with a light and camera. It is often used to diagnose conditions such as ulcers, tumors, and inflammation.
- Colonoscopy: A specific type of endoscopy focused on the colon, allowing the doctor to detect abnormalities such as polyps or cancer.
- Gastroscopy: Similar to an endoscopy, this procedure focuses on examining the upper gastrointestinal tract, including the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
- Enteroscopy: A procedure to examine the small intestine, often used when other tests do not provide a clear diagnosis.
When to See a GI Doctor
It is advisable to consult a GI doctor if you experience symptoms that persist over time or significantly impact your daily life. For example:
- Consistent abdominal pain or discomfort
- Significant changes in bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Frequent bloating or gas
- Persistent heartburn or acid reflux
Preventive Care and Management
GI doctors emphasize the importance of preventive care and lifestyle management in gastrointestinal health. Regular screenings, such as colonoscopies, are crucial for early detection of issues like colorectal cancer. They may also provide advice on dietary modifications, stress management, and medication adherence to manage chronic conditions more effectively. For instance, those with IBS may benefit from a personalized dietary approach, like a low-FODMAP diet, to help alleviate symptoms.
Research and Advances in Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology is a rapidly evolving field, with ongoing research focusing on new treatment modalities, understanding the gut microbiome, and developing better diagnostic tools. Advances in technology, such as capsule endoscopy and artificial intelligence in diagnosing gastrointestinal diseases, are shaping the future of gastrointestinal healthcare. These innovations lead to less invasive procedures and improved patient outcomes, enhancing the overall quality of care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What qualifications does a GI doctor have?
A GI doctor typically holds a Doctor of Medicine (MD) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degree, followed by a residency in internal medicine and a fellowship in gastroenterology. Their education encompasses extensive training in the diagnosis and treatment of GI conditions.
How can I prepare for a visit to a GI doctor?
To prepare for your appointment, you should keep a record of your symptoms, any treatments you’ve undergone, relevant medical history, and a list of medications you’re currently taking. This information will help the doctor make a more accurate diagnosis.
What is the difference between a gastroenterologist and a colorectal surgeon?
A gastroenterologist is a specialist who focuses on non-surgical treatments of gastrointestinal disorders, while a colorectal surgeon performs surgical procedures to treat conditions affecting the intestinal tract, particularly related to colorectal disease.
Are there any risks associated with GI procedures?
As with any medical procedure, there are potential risks associated with diagnostic procedures, including bleeding, infection, and perforation of the digestive tract. However, serious complications are rare, and the benefits often outweigh these risks when performed by a trained professional.
How often should I see a GI doctor?
Your need for visits to a GI doctor will vary depending on your health status and risk factors. Generally, individuals with chronic gastrointestinal issues should have regular check-ups, while those with no symptoms may need routine screening as recommended by their healthcare provider.