Introduction
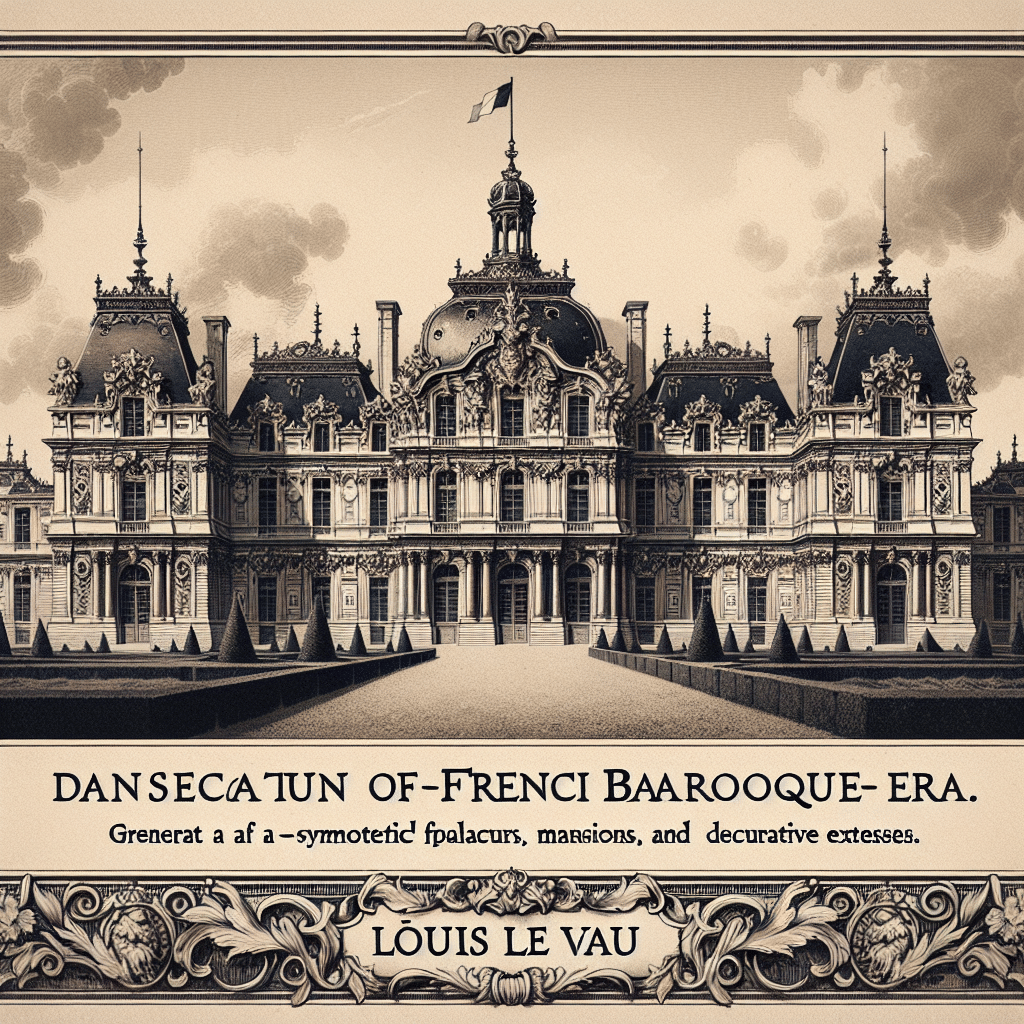
Louis Le Vau, a prominent French architect of the 17th century, is best known for his influential role in shaping the classic architecture of the period. Le Vau was responsible for several key designs that exemplified the Baroque style in France, most notably his work on the Château de Vaux-le-Vicomte. This estate not only showcases his architectural prowess but also laid the groundwork for future developments in French classical architecture, including the more famous Palace of Versailles. Le Vau designed refined spaces characterized by symmetry, grandeur, and harmony with the surrounding landscape. His integration of art and architecture serves as a critical reference point for understanding the evolution of building designs in pre-revolutionary France.
Who was Louis Le Vau?
Born in 1612 in the town of Meaux, Louis Le Vau initially worked under the influence of innovative architectural trends. His training allowed him to study the principles of classical architecture, which he later adapted to fit the unique characteristics of French design.
Le Vau emerged as a leading architect in the court of Louis XIV, the “Sun King,” who was known for his extravagant tastes. His career flourished as he gained royal patronage, leading to numerous prestigious commissions throughout France.
Architectural Contributions
Château de Vaux-le-Vicomte
One of Le Vau’s most significant accomplishments was the design of the Château de Vaux-le-Vicomte, commissioned by Nicolas Fouquet, the Superintendent of Finances. Completed in 1661, the château is renowned for its dramatic use of space, including grand salons, elaborate gardens, and innovative landscaping techniques. The symmetry of the structure along with its expansive grounds showcased Le Vau’s ability to blend architecture with nature. This design not only captivated audiences but also significantly influenced the subsequent construction of Versailles.
Palace of Versailles
Following Vaux-le-Vicomte, Louis XIV commissioned Le Vau to expand and enhance the Palace of Versailles. Although other architects, including André Le Nôtre and François Mansart, were also involved, Le Vau’s influence is evident in the layout and structural design of the palace, which included harmonious proportions and balanced facades.
The addition of the Grand Apartments and the Hall of Mirrors, underscored the opulence and power of the monarchy. Le Vau’s design principles were key in creating a sense of grandeur that defined the French royal architecture of the Baroque period.
Stylistic Elements
Le Vau’s architectural style embodies several essential elements that characterize the Baroque movement. His work is marked by elaborate detailing, bold forms, and a focus on light and shadow play.
His designs often employed classical elements such as columns and pilasters but adapted them to produce a more dynamic aesthetic that emphasized movement and drama. The integration of gardens, such as those at Vaux-le-Vicomte, highlighted his commitment to creating a holistic experience between architecture and the natural world, laying the groundwork for future landscape design.
Legacy and Influence
Louis Le Vau’s contributions to architecture have had a lasting impact. His designs set a standard for future architects in France and beyond, blending functionality with aesthetic appeal. His techniques and approaches became reference points in architectural education and practice.
The principles he employed in his works, particularly the seamless merging of built and natural environments, continue to influence contemporary landscape and architectural design. Le Vau’s legacy is preserved not only in the buildings he created but also in the inspiration it provides for ongoing architectural innovations.
Criticism and Counterarguments
While Le Vau is celebrated for his architectural contributions, some historians suggest that his work was not without its critics. Discussions around the sustainability of his designs have surfaced, particularly the extensive use of resources for grandiose structures. Some have argued that his creations emphasized aesthetics over practicality, potentially leading to costly maintenance and preservation challenges later on.
Nonetheless, most experts agree that his artistic vision and mastery of space have produced enduring monuments of cultural significance. The popularity of Versailles, among others, speaks to the successful blending of beauty, utility, and environmental consideration despite any criticisms regarding resource management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What motivated Louis Le Vau’s architectural style?
Louis Le Vau was motivated by the desire to create structures that embodied the strength and authority of the monarchy while ensuring harmony with nature. His studies of classical architecture led him to innovate within the Baroque style, which emphasized grandeur and elegance.
How did Le Vau’s work influence future architects?
Le Vau’s work influenced future architects through his innovative blending of architecture and landscaping, particularly seen in his designs for Vaux-le-Vicomte and Versailles. These principles inspired subsequent generations in both France and abroad, leading to a broader acceptance of integrated design approaches.
What are some of Le Vau’s other notable works?
In addition to Vaux-le-Vicomte and his contributions to Versailles, Louis Le Vau was involved in the design of several churches and other aristocratic residences. Notable examples include the Church of Saint-Sulpice in Paris and the Château de Chantilly.
Why is Louis Le Vau considered a significant figure in architecture?
Louis Le Vau is considered significant due to his pioneering role in the development of French Baroque architecture, which combined traditional classical motifs with innovative design approaches. His work laid the foundation for one of France’s architectural masterpieces, significantly influencing Western architectural trends.