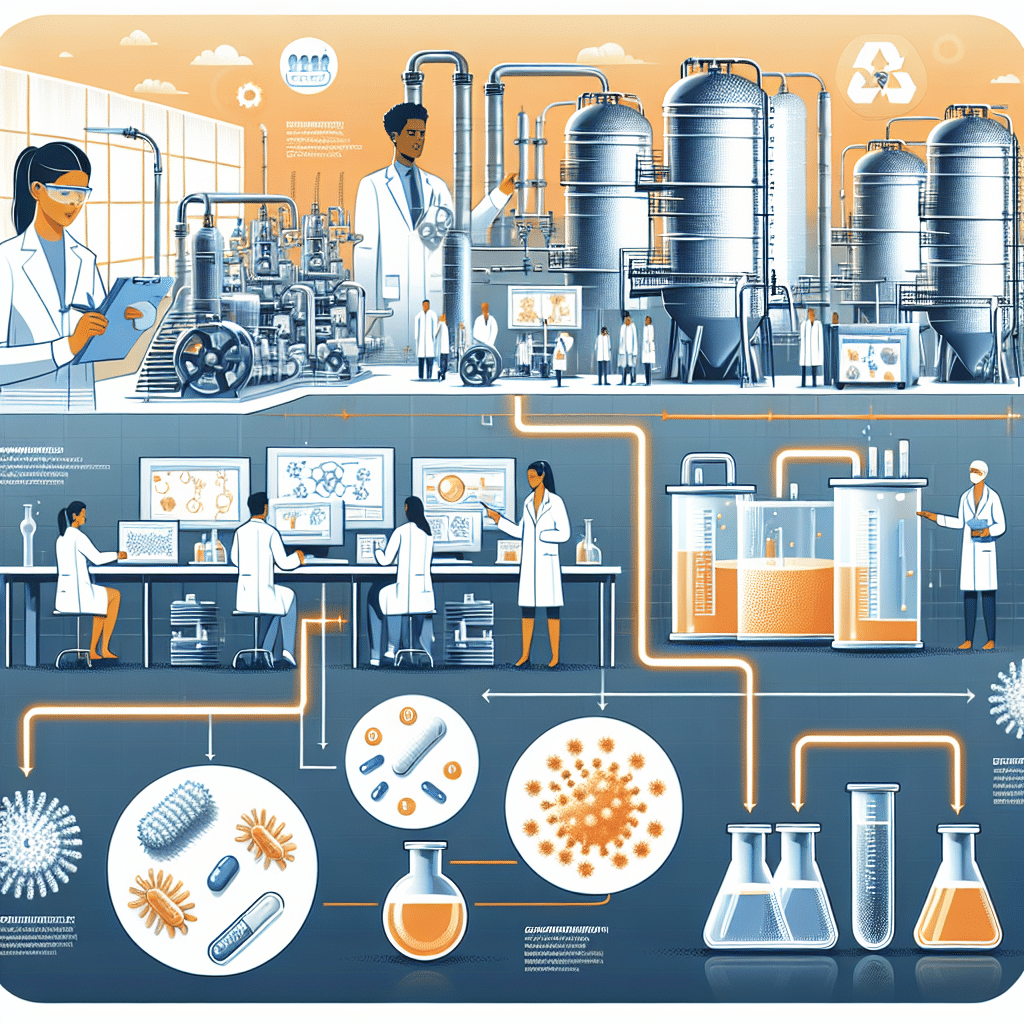
Introduction to Biomanufacturing
Biomanufacturing is a process that leverages biological systems, such as living cells or microorganisms, to produce valuable products, ranging from pharmaceuticals and enzymes to biofuels and agricultural chemicals. This innovative approach harnesses the capabilities of nature by using organisms that can convert raw materials into useful substances through biochemical processes. The resulting products are often more sustainable, environmentally friendly, and efficient compared to traditional manufacturing techniques. In essence, biomanufacturing plays a vital role in creating a circular economy where waste is minimized, and resources are utilized effectively. Understanding biomanufacturing not only opens avenues for advancements in biotechnology but also addresses critical global challenges like health care, energy demands, and food security.
Understanding Biomanufacturing
At its core, biomanufacturing integrates biological principles with manufacturing practices. This multidisciplinary field combines elements from biology, chemistry, engineering, and computer science to optimize production processes that use living organisms. These organisms can include bacteria, yeast, fungi, plant cells, and even animal cells. By manipulating their metabolic pathways, scientists and engineers can enhance their ability to produce desired compounds.
The Role of Microorganisms
Microorganisms are the workhorses of biomanufacturing. They are selected for their ability to synthesize specific products efficiently. For example, E. coli is commonly used to produce proteins, while yeast species like Saccharomyces cerevisiae are utilized in beer and wine production. Other types of microorganisms play crucial roles in producing enzymes that catalyze chemical reactions, essential in industries like food processing and textiles. Each microorganism’s specific characteristics are exploited to improve yield and reduce production times.
Types of Products in Biomanufacturing
Biomanufacturing encompasses a wide variety of sectors and products. Some key categories include:
- Pharmaceuticals: Drugs produced via biomanufacturing, including monoclonal antibodies and vaccines, have transformed the healthcare sector. The production of insulin using recombinant DNA technology is a prime example.
- Enzymes: Used across multiple industries, enzymes made through biomanufacturing facilitate processes in food manufacturing, detergents, and biofuels.
- Biofuels: An emerging area, biofuels produced from plant and microbial sources can replace fossil fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Biopolymers: Sustainable alternatives to petroleum-based plastics created using microorganisms, contributing to the reduction of plastic waste.
Biomanufacturing Process Overview
The biomanufacturing process can be broken down into several stages:
- Selection of Organisms: Choosing the right microorganism based on the desired end product and efficiency in biochemical pathways.
- Fermentation: The selected organisms are cultivated in controlled environments that promote growth and production.
- Harvesting: Post-fermentation, the desired product is separated from the biomass.
- Purification: The final stage involves refining the product to attain the necessary purity and quality standards.
Benefits of Biomanufacturing
Biomanufacturing offers several significant advantages:
- Sustainability: Biological processes are often more sustainable, reducing dependency on non-renewable resources.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Bioprocesses typically generate less waste and harmful emissions compared to traditional manufacturing.
- Innovation: Continuous advancements in biotechnology enhance product range and processes.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, biomanufacturing faces challenges:
- Complexity: Biological systems can be unpredictable, making process optimization challenging.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The biomanufacturing industry is subject to stringent regulations to ensure safety and efficacy, which can slow down product development.
- High Initial Costs: Setting up biomanufacturing facilities can be capital-intensive.
Future of Biomanufacturing
The future of biomanufacturing is promising. With advancements in synthetic biology and genetic engineering, manufacturers are poised to achieve higher efficiency and reduced costs. Emerging technologies, such as CRISPR and automation, facilitate the design of microorganisms tailored for specific tasks, further enhancing biomanufacturing capabilities. As the global demand for sustainable products rises, biomanufacturing is positioned to play a crucial role in meeting these needs, fostering an innovative and sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is biomanufacturing?
Biomanufacturing is the use of biological systems, such as microorganisms or living cells, to produce valuable products through biochemical processes.
What are the common products produced by biomanufacturing?
Common products include pharmaceuticals (like vaccines and insulin), enzymes, biofuels, and biopolymers.
What are the advantages of biomanufacturing over traditional methods?
Advantages include sustainability, reduced environmental impact, lower waste generation, and the ability to create innovative products.
What challenges does biomanufacturing face?
Challenges include the complexity of biological systems, regulatory hurdles, and high initial investment costs.
How is biomanufacturing regulated?
The biomanufacturing industry is regulated by agencies such as the FDA in the United States, which ensures that products are safe and effective for consumer use.
What is the future of biomanufacturing?
The future is promising due to advancements in genetic engineering and synthetic biology, which are expected to increase efficiency and expand the types of products that can be made.
Conclusion
Biomanufacturing represents a transformative approach to production, harnessing the power of biological systems for sustainable and efficient manufacturing. As industries continue to evolve and the demand for environmentally friendly solutions increases, biomanufacturing stands at the forefront, offering innovative pathways to address global challenges. By embracing the potential of this field, we can look forward to a more sustainable and healthy future.