Introduction to Fish Roe
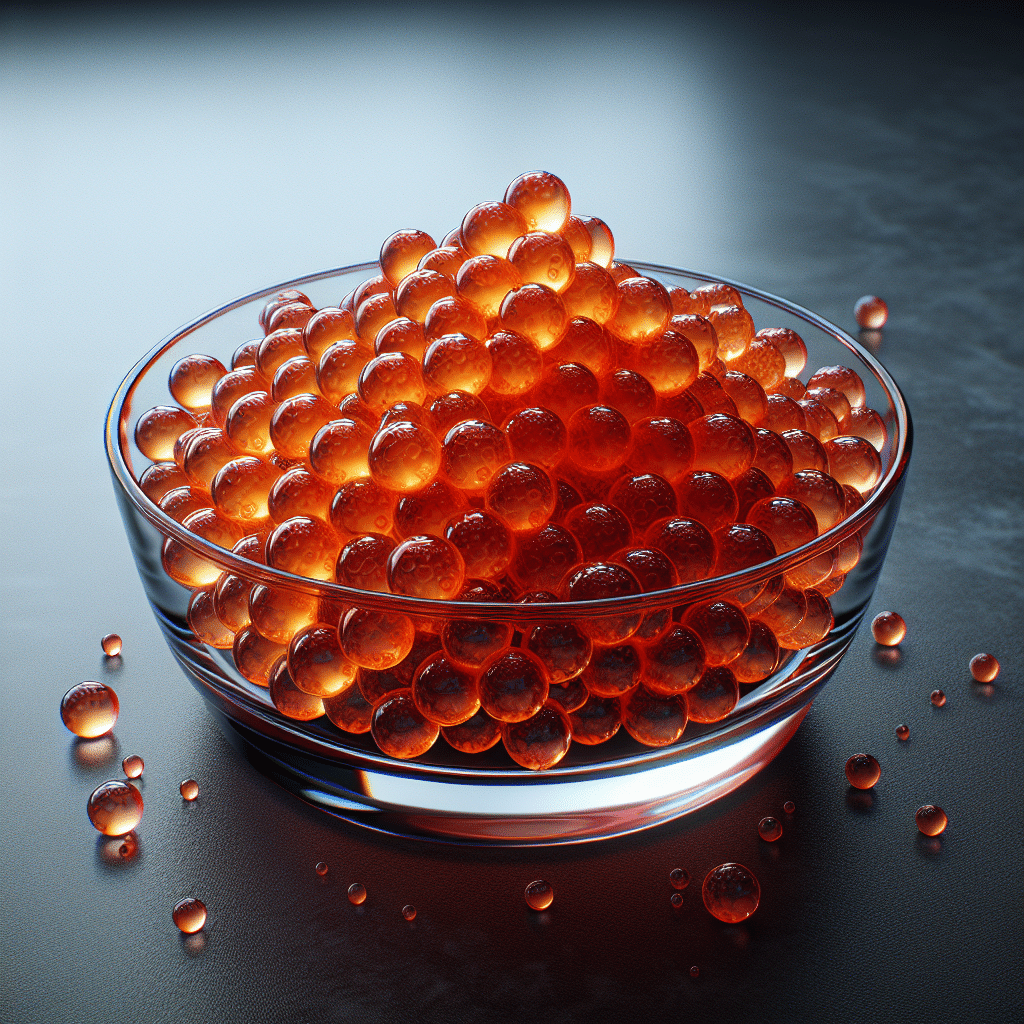
Fish roe, commonly referred to as fish eggs, represents the reproductive material of female fish. This delicacy varies widely in color, size, and flavor, depending on the species from which it originates. Fish roe is often used in numerous culinary applications, ranging from sushi and spreadable caviar to garnishing dishes. Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, proteins, and vital vitamins, it is celebrated for its health benefits besides its distinctive taste. Available in various forms like caviar (from sturgeon), ikura (salmon roe), and tobiko (flying fish roe), it is enjoyed across cultures, making it a favored ingredient in gourmet cuisine. Understanding fish roe’s nutritional value, types, and culinary uses can enhance your appreciation of this unique aquatic offering.
What is Fish Roe?
Fish roe refers to the eggs or the egg mass that female fish produce during their reproductive cycle. These eggs are typically characterized by a gelatinous texture and vibrant colors that can range from soft orange to dark black. Fish roe serves as a vital nutrient source for fish species, helping young fish to develop and survive in aquatic environments.
The Nutritional Value of Fish Roe
Fish roe is not just a culinary delight but also a powerhouse of nutrition. It is rich in:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Essential for heart health, brain function, and reducing inflammation.
- Proteins: Crucial for muscle repair and growth, containing essential amino acids.
- Vitamins: High levels of vitamins A, B12, and D which support various bodily functions.
- Minerals: Contains iron, zinc, magnesium, and selenium that promote overall health.
Types of Fish Roe
Fish roe comes from various species, each type possessing unique flavors and textures. Below are some of the most popular types:
Caviar
Caviar is often considered the most luxurious type of fish roe, collected predominantly from sturgeon species. It’s known for its delicate texture and rich, briny flavor. Genuine caviar is graded based on the fish species and processing methods.
Ikura
Ikura refers to salmon roe and is widely used in Japanese cuisine. It is noted for its large size, vibrant orange color, and slightly sweet flavor profile. Ikura is often marinated in soy sauce before consumption.
Tobiko
Tobiko is the roe from flying fish, commonly found in sushi. Tobiko has a crunchy texture and can be colored with natural ingredients, creating visually appealing dishes.
Masago
Masago, or capelin roe, is smaller and less expensive than tobiko. Masago is often used in sushi rolls and is known for its slightly salty taste and crunchy texture.
Other Roes
Other species such as trout, mackerel, and lumpfish also produce roe that is utilized in different culinary practices around the world.
Culinary Uses of Fish Roe
Fish roe is a versatile ingredient that enhances dishes with its unique flavors, textures, and visual appeal. Here are some common culinary applications:
Sushi and Sashimi
Fish roe plays an integral role in sushi and sashimi dishes. Its bold flavors complement the mild taste of rice and fish.
Garnishes
Chefs often use fish roe to garnish salads, pasta, and seafood dishes, adding both flavor and the aesthetic appeal of vibrant colors.
Spreads and Dips
Fish roe can be blended into spreads, such as the classic caviar butter or flavored cream cheese, perfect for crackers and bagels.
Spicy Groups
Cooked and spiced fish roe can be served as a side dish or a main course component, showcasing their adaptability in a range of culinary practices.
How to Select and Store Fish Roe
Selecting high-quality fish roe involves understanding the freshness and source. Here are some tips:
Choosing the Right Fish Roe
- Look for vibrant color without any discoloration.
- Smell for freshness; it should not have a strong fishy odor.
- Check the packaging date to ensure it’s within the expiration timeline.
Storage Tips
Proper storage is crucial for maintaining the quality of fish roe:
- Keep unopened roe in the refrigerator, ideally at temperatures below 40°F (4°C).
- Once opened, consume it within a few days, refrigerating in a tightly sealed container.
Health Considerations and Allergies
While fish roe is generally safe for consumption, some individuals may experience allergies, particularly those with fish or shellfish allergies. It is vital to be aware of the ingredients and consult a healthcare professional if unsure.
Environmental and Sustainability Issues
Concerns around overfishing and habitat loss are significant in the caviar production industry. Choosing roe from sustainable sources, compliant with guidelines such as those set forth by the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC), can help mitigate these issues.
FAQs about Fish Roe
1. What is the difference between caviar and roe?
Caviar specifically refers to roe harvested from sturgeon species, while roe can refer to the eggs from any fish species.
2. Is fish roe healthy to eat?
Yes, fish roe is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, proteins, vitamins, and minerals, which contribute positively to health.
3. Can I freeze fish roe?
While it is discouraged to freeze fish roe due to texture changes, some types can be frozen if properly sealed.
4. How long does fish roe last?
Unopened fish roe typically lasts several months if stored properly in the refrigerator. Opened roe should be consumed within a few days.
Conclusion
Fish roe is more than just a gourmet treat; it is a nutrient-dense food that has captivated taste buds around the world. By understanding its types, culinary uses, and health benefits, you can appreciate the complexity and elegance that fish roe brings to the culinary landscape. Whether you’re interested in fine dining or looking to enhance your home cooking, incorporating fish roe can elevate your dining experience to new heights.