What is Layer Palletizing?
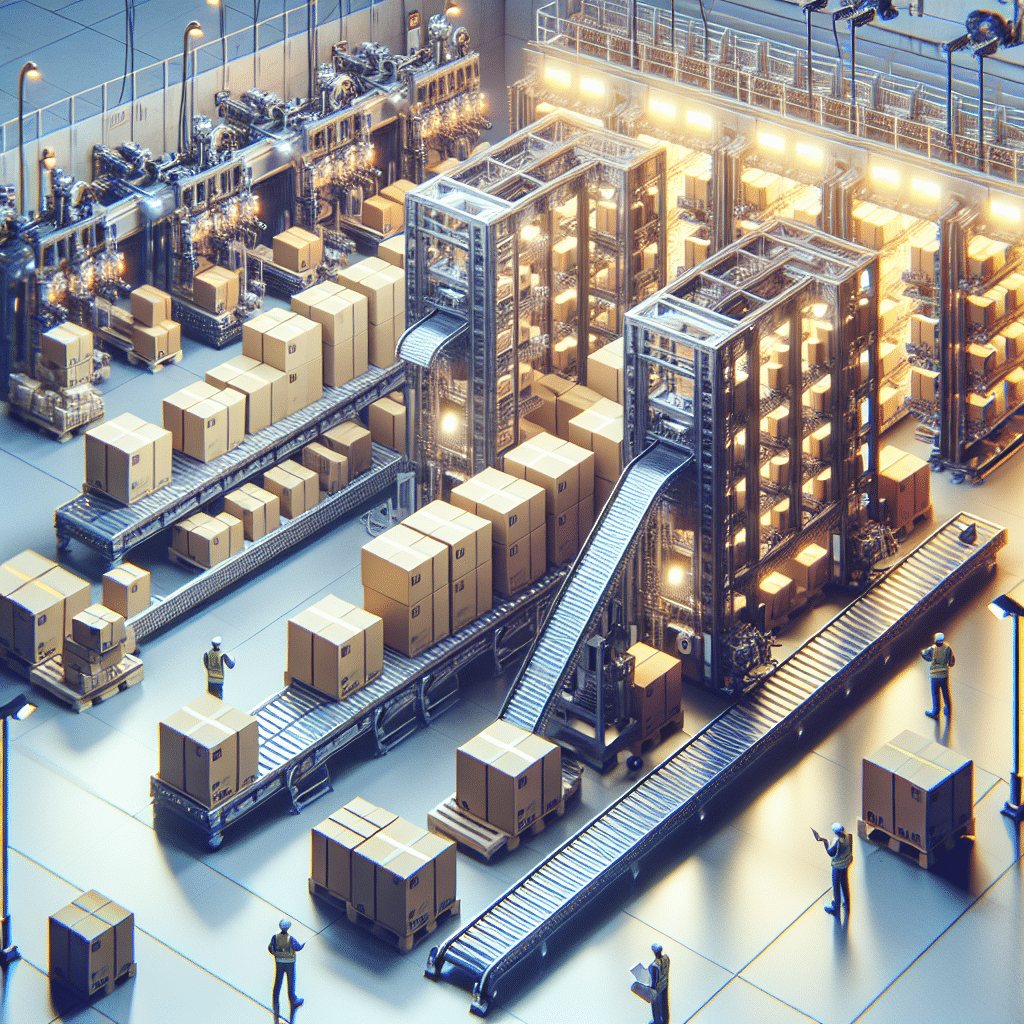
Layer palletizing is an automated process used in logistics and warehousing that involves stacking goods according to prescribed layers onto a pallet for storage or shipping. This method is crucial for enhancing efficiency and optimizing space utilization, especially in warehouses where goods need to be stored safely while maximizing accessibility. In layer palletizing, products are grouped by layer before being moved to a pallet, ensuring that the arrangement is stable and uniform. This technique can significantly reduce labor costs and improve speed in handling bulky items, providing benefits to various industries, including food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and consumer goods. With the implementation of robotics and modern technology, layer palletizing solutions have become more sophisticated, allowing for greater precision and adaptability in operations.
Understanding Layer Palletizing
Definition and Objective
Layer palletizing is defined as the arrangement of products in horizontal layers before placing them onto a pallet. The primary objective of this system is to efficiently prepare goods for transportation while maximizing the use of space. By stacking products in a systematic manner, companies can enhance stability during transit, reduce shipping costs, and simplify the handling and storage of inventory.
Importance in Supply Chain Management
Layer palletizing plays a pivotal role in the supply chain management process. The advantages include:
- Optimization of Space: By arranging products in layers, the available storage space is used more effectively, minimizing wasted areas.
- Increased Efficiency: Layer palletizing speeds up the packing process, allowing for quicker turnaround times in distribution.
- Improved Safety: Properly palletized goods are less likely to become unstable during transport, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Cost Reduction: Automated processes help to lower labor costs typically associated with manual palletizing.
Types of Layer Palletizing
Manual vs. Automated Layer Palletizing
Layer palletizing can be classified into two main types: manual and automated systems.
- Manual Layer Palletizing: Involves human workers stacking items according to specific layer patterns. While this method allows for flexibility and can handle various shapes and sizes, it is more time-consuming and prone to human error.
- Automated Layer Palletizing: This technology utilizes specialized equipment, such as robotic arms or conveyor systems, to stack products onto pallets. Automated systems significantly increase speed, consistency, and efficiency compared to manual processes.
Robotic Layer Palletizing
Robotic layer palletizing is a sub-category of automated layer palletizing that uses robotic systems to handle and stack products. These robotics are equipped with advanced vision systems, sensors, and manipulation technologies, ensuring precise stacking of goods. This method is particularly beneficial for high-volume operations, where speed and accuracy are paramount.
Key Components of Layer Palletizing Systems
Pallets
High-quality pallets made from materials such as wood, plastic, or metal are essential for effective layer palletizing. The selected pallet type must bear the load of the products being stacked and withstand transport conditions.
Conveyor Systems
To enhance the flow of goods to the palletizing area, conveyor systems are often integrated into layer palletizing. These systems facilitate the continuous movement of products, reducing the time taken for each palletizing cycle.
Control Systems
Automated systems require sophisticated control panels that manage the operation of machinery and ensure synchronization between product feeding, stacking, and pallet movement.
Benefits of Layer Palletizing
Layer palletizing provides numerous benefits to manufacturing and logistics operations:
- Enhanced Productivity: Automated systems minimize downtime and increase output.
- Improved Accuracy: Reduces errors associated with manual handling.
- Consistency: Automated processes ensure uniformity in the stacking of products.
- Flexibility: Systems can typically be programmed to handle multiple products and layer configurations.
Challenges and Considerations
Space Limitations
While layer palletizing significantly optimizes storage, it also requires a certain amount of space for machinery and conveyors, which may not be feasible for all operations.
Cost of Automation
The initial investment in robotic and automated systems can be significant. However, the long-term savings in labor and increased efficiency often justify this expense.
Industry Best Practices
To ensure the successful implementation of layer palletizing, consider the following best practices:
- Conduct a Needs Assessment: Understand specific operational requirements before choosing a layer palletizing system.
- Invest in Training: Proper training for operators of automated systems is essential to maximize efficiency and safety.
- Regular Maintenance: Maintain equipment to prevent breakdowns and ensure reliability.
- Evaluate Space Utilization: Regular assessments of storage and handling spaces can improve efficiency over time.
Application Across Industries
Layer palletizing is prevalent in various sectors, including:
- Agriculture: Handling bulk products like grains and produce.
- Food and Beverage: Packing cases of beverages and packaged foods.
- Consumer Goods: Efficiently stacking household items and personal care products.
Future Trends in Layer Palletizing
As companies continue to seek efficiency, layer palletizing is expected to evolve. Current trends include:
- Integration of AI: Enhanced decision-making capabilities for inventory management.
- Enhanced Customization: Systems that adapt to specific product shapes and sizes.
- Increased Sustainability: Using eco-friendly materials for pallets and reduced energy consumption in automated systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What types of products can be layer palletized?
Layer palletizing is suitable for various products, including packaged goods, bottles, boxes, and other stable items that can be stacked in layers.
2. How does automated layer palletizing compare to manual methods?
Automated layer palletizing is faster, more consistent, and less prone to human error than manual methods, making it ideal for high-volume operations.
3. Can layer palletizing systems be customized?
Yes, many layer palletizing systems can be programmed to accommodate different product types and dimensional requirements, allowing for flexible operations.
4. What industries most frequently use layer palletizing?
Industries like food and beverage, consumer goods, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals commonly utilize layer palletizing due to their need for efficient packaging and distribution.
5. What are the main components of a layer palletizing system?
The key components typically include pallets, conveyor systems, and control systems for automation.