Introduction
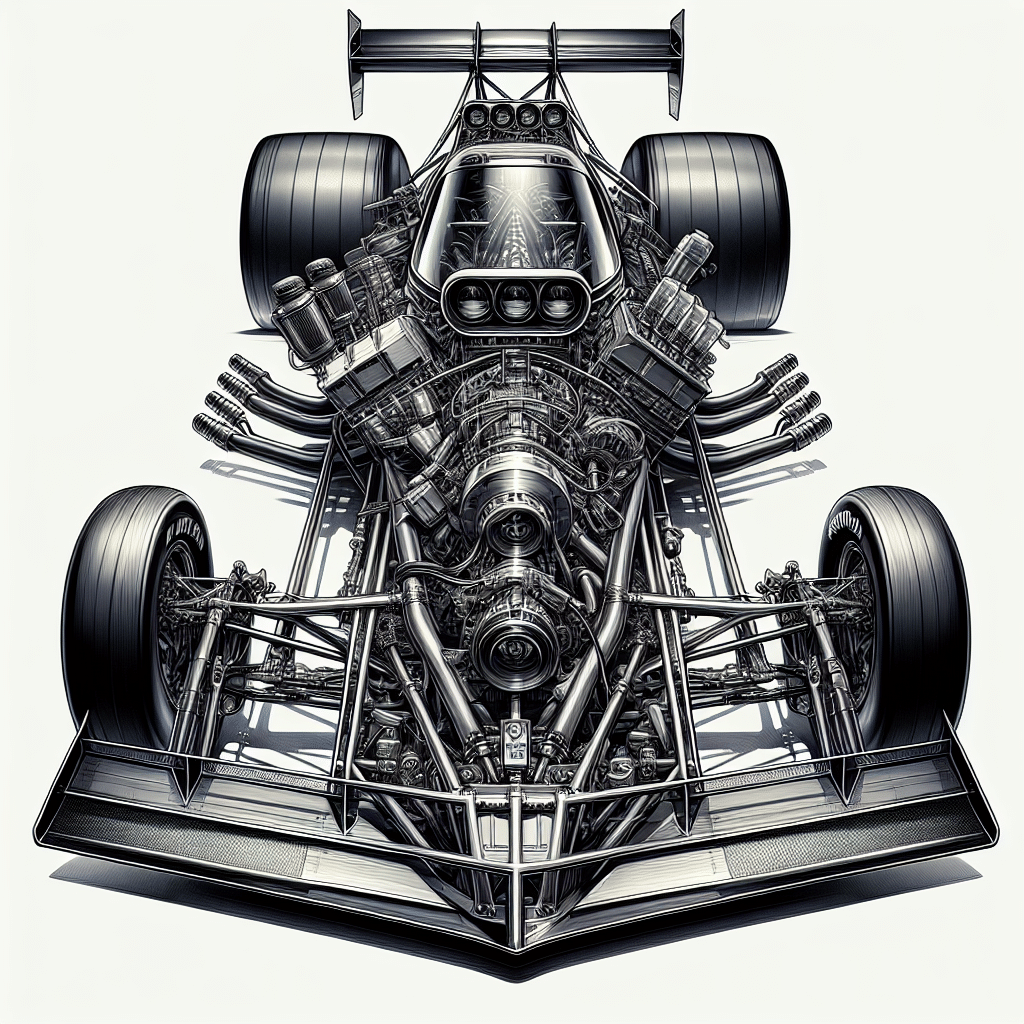
The cowl of a Top Fuel dragster is a crucial aerodynamic component located on the front section of the vehicle, just behind the front wing and before the driver’s compartment. This structure plays a significant role in managing airflow and enhancing the dragster’s performance during high-speed runs. Designed to direct air over and around the car, the cowl helps reduce drag, improve stability, and assist in maintaining aerodynamic efficiency. In high-stakes racing, where mere fractions of a second can determine the winner, the cowl’s design is meticulously engineered to optimize airflow dynamics. Understanding the cowl’s functions and specifications is essential for fans and aspiring drag racers alike, as it reflects the advanced engineering and tech that enhance Top Fuel dragster performance.
Understanding the Cowl Structure
The cowl, often referred to as the “cowl panel” or “cowl area,” serves as a bridge between the dragster’s chassis and aerodynamic bodywork. Designed to manage and streamline airflow, it helps minimize turbulence and drag during a race. The specific design and materials used in constructing the cowl can vary based on the team’s aerodynamic goals and engineering philosophies. The cowl’s shape often mimics that of an aircraft wing, as both share the need to effectively manipulate airflow for optimal performance.
Key Functions of the Cowl
Aerodynamics
The primary purpose of the cowl is to enhance the aerodynamic efficiency of the dragster. By directing airflow in a way that minimizes drag and maximizes downforce, the cowl significantly impacts the vehicle’s speed and control. The design of the cowl can reduce lift, which is particularly important when achieving extreme speeds where lift can compromise stability.
Cooling Airflow
Another critical function of the cowl is to channel cooling airflow to key engine components. In drag racing, where engines can reach extremely high temperatures, ensuring adequate cooling is vital. The cowl incorporates ventilation features designed to allow cool air to flow over the engine and other heat-sensitive parts. This cooling aspect not only improves performance but also extends the lifespan of engine components.
Driver Protection
Beyond aerodynamic efficiency, the cowl provides a degree of protection to the driver. Its structure aids in deflecting debris and minimizing the impact of wind forces at high speeds. Racing at over 300 mph exposes drivers to significant wind forces and potential hazards, making the design of the cowl vital for safety.
Materials and Construction
Modern Top Fuel dragsters typically use advanced composite materials for their cowls. These materials are chosen for their lightweight and high strength properties, allowing for robust performance while minimizing weight. Carbon fiber and fiberglass are common choices, providing the balance of structural integrity and aerodynamic shape.
Design Variations
Different racing teams may implement unique design variations on their cowls, influenced by specific aerodynamic goals, track conditions, or design philosophies. Some teams may opt for larger, more pronounced cowls to increase airflow management, while others might favor a sleeker, more streamlined approach. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and wind tunnel testing are often employed to analyze and refine the cowl’s design before it’s put to the test on the drag strip.
Impact on Performance
The cowl’s design can have a direct impact on a dragster’s performance metrics, including acceleration, stability, and overall speed. Any alterations to the cowl structure can result in variations in the car’s drag coefficient, influencing how quickly it can cover the quarter-mile track. Teams that work meticulously on optimizing the cowl have often reported significant performance improvements, reflecting its importance in competitive drag racing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What specific aerodynamic benefits does the cowl provide?
The cowl helps to minimize drag and maintain stability, thereby improving the overall speed of the dragster during races. It directs airflow to maximize downforce and reduce lift, which is crucial for handling at high speeds.
2. How does the cowl affect engine cooling?
The cowl is designed to channel air to critical engine components, helping to dissipate heat more effectively, which is essential during intense racing conditions.
3. Are all cowls the same across different Top Fuel teams?
No, cowl designs can vary significantly between teams. Each team may customize its cowl to fit its aerodynamic strategy or specific performance needs, often influenced by extensive wind tunnel testing and computational simulations.
4. What materials are commonly used in constructing dragster cowls?
Advanced composite materials, predominantly carbon fiber and fiberglass, are used for their lightweight and high-strength properties, which help optimize performance without adding unnecessary weight to the vehicle.
5. How do teams test and optimize cowl designs?
Teams typically utilize computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations and wind tunnel testing to analyze airflow and performance characteristics of their cowl designs before implementing changes on the dragstrip.