Introduction
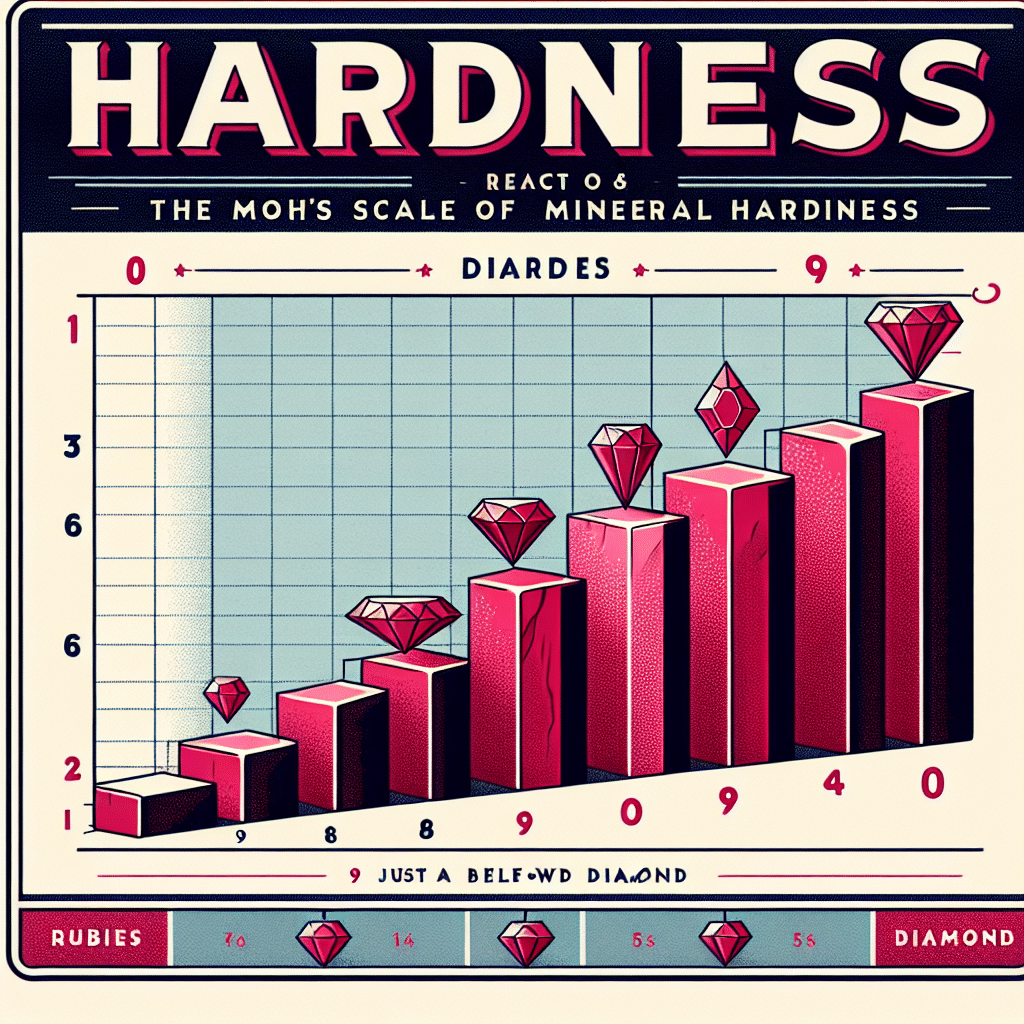
The hardness of rubies is primarily measured using the Mohs hardness scale, a system that ranks minerals based on their scratch resistance. Rubies, which are a variety of the mineral corundum, achieve a hardness of 9 on this scale, making them exceptionally durable and one of the hardest gemstones available. This places them just below diamonds, which score a perfect 10. The high hardness of rubies is one of the reasons they are prized in jewelry and utilized in industrial applications, such as cutting and grinding tools. Understanding the hardness scale for rubies not only highlights their strength but also informs choices for care and maintenance in jewelry-making and gemstone collection.
Understanding the Mohs Hardness Scale
The Mohs hardness scale, developed by German mineralogist Friedrich Mohs in 1812, categorizes minerals based on their ability to scratch one another. Each mineral is assigned a relative value from 1 (talc, the softest) to 10 (diamond, the hardest). The scale is not linear; it is a comparative system to help identify the hardness of a mineral rather than measure it precisely.
Hardness of Rubies
Rubies, possessing a hardness of 9, are noted for their robustness and ability to withstand wear and tear, which is why they are often used in rings and other jewelry that endure daily use. This extraordinary hardness is attributed to the crystal structure of corundum, which is formed from aluminum oxide (Al2O3) with trace amounts of chromium, giving rubies their characteristic red color.
Comparative Hardness of Minerals
To appreciate the significance of a ruby’s hardness, it is essential to compare it with other commonly known minerals:
- Diamond (10): The hardest known natural material.
- Corundum (9): Includes sapphires and rubies.
- Topaz (8): A commonly found gemstone.
- Quartz (7): Found in a variety of natural settings.
Practical Implications of Ruby Hardness
Understanding the hardness of rubies has significant implications, particularly in the fields of jewelry design and maintenance. Due to their high resilience, rubies are less susceptible to scratches compared to softer gemstones, making them ideal for use in rings, bracelets, and other settings subjected to frequent wear. Regular cleaning can preserve their brilliance but should avoid abrasive substances that could scratch them.
Care and Maintenance for Ruby Jewelry
Despite their hardness, rubies still require proper care. Here are some tips to ensure the longevity of ruby jewelry:
- Avoid harsh chemicals: Clean your rubies with mild soap and water.
- Store carefully: Keep rubies in a separate compartment to avoid scratches from harder materials.
- Regular inspections: Check settings and mountings to ensure stones remain secure.
Applications of Rubies Beyond Jewelry
In addition to their aesthetic appeal, rubies play a crucial role in various industrial applications given their hardness. They are used in laser technology, watchmaking, and even as abrasives in cutting tools. Their ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures makes them valuable in high-tech fields.
FAQs about Ruby Hardness
1. What is the importance of a gemstone’s hardness?
The hardness of a gemstone impacts its durability, scratch resistance, and suitability for various types of jewelry. Harder stones, like rubies, are generally preferred for items worn daily.
2. Are there treatments that affect a ruby’s hardness?
Some rubies undergo treatments, such as heat treatment, to enhance color and clarity. These treatments do not typically affect the stone’s hardness but may affect durability depending on the method used.
3. Can rubies be chipped or broken?
While rubies are highly durable, they can still chip or break under extreme force or if hit at the right angle. It’s essential to handle ruby gemstones with care to avoid damage.
4. How does rubies’ hardness compare to other gemstones?
Rubies are one of the hardest gemstones, scoring 9 on the Mohs scale. This places them above many other popular stones like emeralds (7.5-8) and opals (5-6), making them a suitable choice for jewelry that is subject to significant wear and tear.
5. What factors affect the lifespan of ruby jewelry?
Factors affecting the lifespan of ruby jewelry include exposure to harsh chemicals, environmental elements, and the frequency of wear. Regular maintenance and proper storage can significantly enhance their longevity.
Conclusion
Rubies are not only beautiful but also exceptionally hard, achieving a score of 9 on the Mohs hardness scale. This high level of durability makes them a favored choice for both fine jewelry and industrial applications. By understanding the properties of rubies, you can appreciate their value and beauty more fully, as well as ensure their longevity through proper care.