Introduction
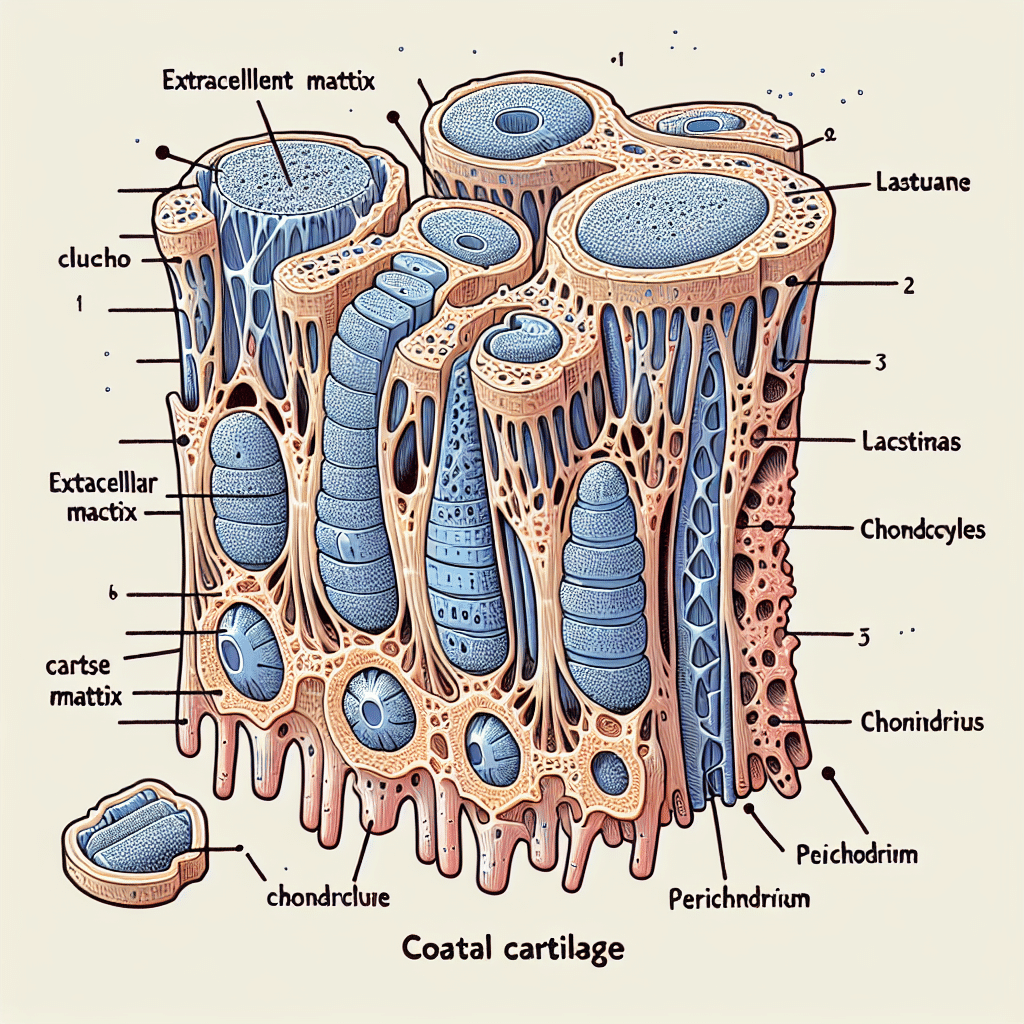
Costal cartilage is a type of hyaline cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum (breastbone) in the human body. It plays a crucial role in providing flexibility and support to the ribcage, contributing to the respiratory process by allowing the chest to expand and contract. Hyaline cartilage, characterized by its glassy, smooth appearance, contains a high proportion of collagen fibers, providing both strength and resilience. Understanding the structure and function of costal cartilage is essential for appreciating its importance in maintaining respiratory health and ribcage stability.
Understanding Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary tissue types in the human body, the others being epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissues. It serves several essential functions, including providing structural support, binding tissues together, protecting organs, and storing energy. Connective tissue is broadly classified into two main categories: loose connective tissue (like adipose and areolar tissue) and dense connective tissue (like tendons and ligaments). Within these categories, we find specialized tissues, including cartilage, bone, blood, and adipose tissue.
Types of Cartilage
Cartilage is a specialized form of connective tissue characterized by a gelatinous matrix composed of collagen and elastin fibers, which provide strength and flexibility. There are three primary types of cartilage:
- Hyaline Cartilage: This is the most abundant type, found in locations such as the costal cartilages, nose, trachea, larynx, and the ends of long bones. It provides smooth surfaces for joint movement, flexibility, and support.
- Elastic Cartilage: This type contains more elastin fibers, making it more flexible. It is found in structures like the ear and epiglottis.
- Fibrocartilage: This type has a higher density of collagen fibers, providing strength and support in areas subjected to heavy pressure, such as intervertebral discs and the pubic symphysis.
Characteristics of Costal Cartilage
Costal cartilage is specifically composed of hyaline cartilage, making it unique in its structure and purpose. Here are some key characteristics:
- Location: Costal cartilage connects the anterior ends of the ribs to the sternum, forming the costal arch.
- Elasticity: The cartilage provides the necessary elasticity for the ribcage, allowing for expansion during inhalation and contraction during exhalation.
- Durability: While flexible, costal cartilage is also durable enough to resist compression and bending forces.
The Role of Costal Cartilage in Respiration
The primary role of costal cartilage is to support the anatomy of the ribcage while allowing for necessary movement during the respiratory cycle. When we inhale, the diaphragm contracts, and the ribcage expands. Costal cartilage enables this expansion without compromising structural integrity, allowing for efficient breathing. In individuals with conditions affecting the ribcage or cartilage (such as costochondritis), the ability to breathe comfortably may be impaired, showcasing the critical function of this connective tissue.
Common Disorders Related to Costal Cartilage
Over time, costal cartilage and the associated structures can be subjected to wear and tear, leading to various disorders:
- Costochondritis: This is an inflammation of the costal cartilage, often resulting in localized pain and tenderness. It can be induced by repetitive trauma or excessive physical activity.
- Arthritis: As one ages, degenerative changes can occur in the cartilage, including the costal cartilage, leading to stiffness and pain in the ribcage region.
- Fractures: Direct trauma to the chest can cause rib fractures and associated damage to the adjacent costal cartilage, leading to pain and difficulty in movement.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Costal Cartilage Disorders
Upon experiencing pain or discomfort in the chest area, it is critical to seek medical advice. Diagnosis often includes physical examinations, medical history reviews, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs. Treatment strategies may include:
- Rest and Ice Therapy: Reducing activity and applying ice can alleviate inflammation and pain.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises designed to strengthen and stabilize the chest wall may be recommended.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged cartilage.
Prevention of Costal Cartilage Issues
Preventing issues related to costal cartilage primarily revolves around maintaining overall health and avoiding undue stress on the ribcage. Regular exercise, proper body mechanics during physical activity, and good posture can all contribute to the health of costal cartilage. Additionally, engaging in activities that promote flexibility and strength can help maintain the elasticity and durability of the connective tissue.
Conclusion
Costal cartilage is a vital type of hyaline cartilage that offers both structural and functional support to the ribcage, significantly influencing respiratory health. Understanding its role, characteristics, and potential disorders can assist in recognizing its importance and addressing any issues that may arise over time.
FAQ
What is costal cartilage made of?
Costal cartilage is primarily composed of hyaline cartilage, which contains a matrix of collagen fibers and a gel-like substance that provides flexibility and strength.
How many costal cartilages are there?
There are typically 12 pairs of ribs in humans, each connected to the sternum via costal cartilage, resulting in a total of 12 costal cartilages.
Can costal cartilage be damaged?
Yes, costal cartilage can sustain injury due to trauma, repetitive strain, or conditions like costochondritis, leading to pain and discomfort.
How does costal cartilage support breathing?
Costal cartilage allows for the expansion and contraction of the ribcage during breathing by providing the necessary elasticity and strength to maintain the structure of the chest.
What treatment options are available for costal cartilage disorders?
Treatment options may include rest, ice therapy, NSAIDs, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery if the cartilage is severely damaged.