Introduction
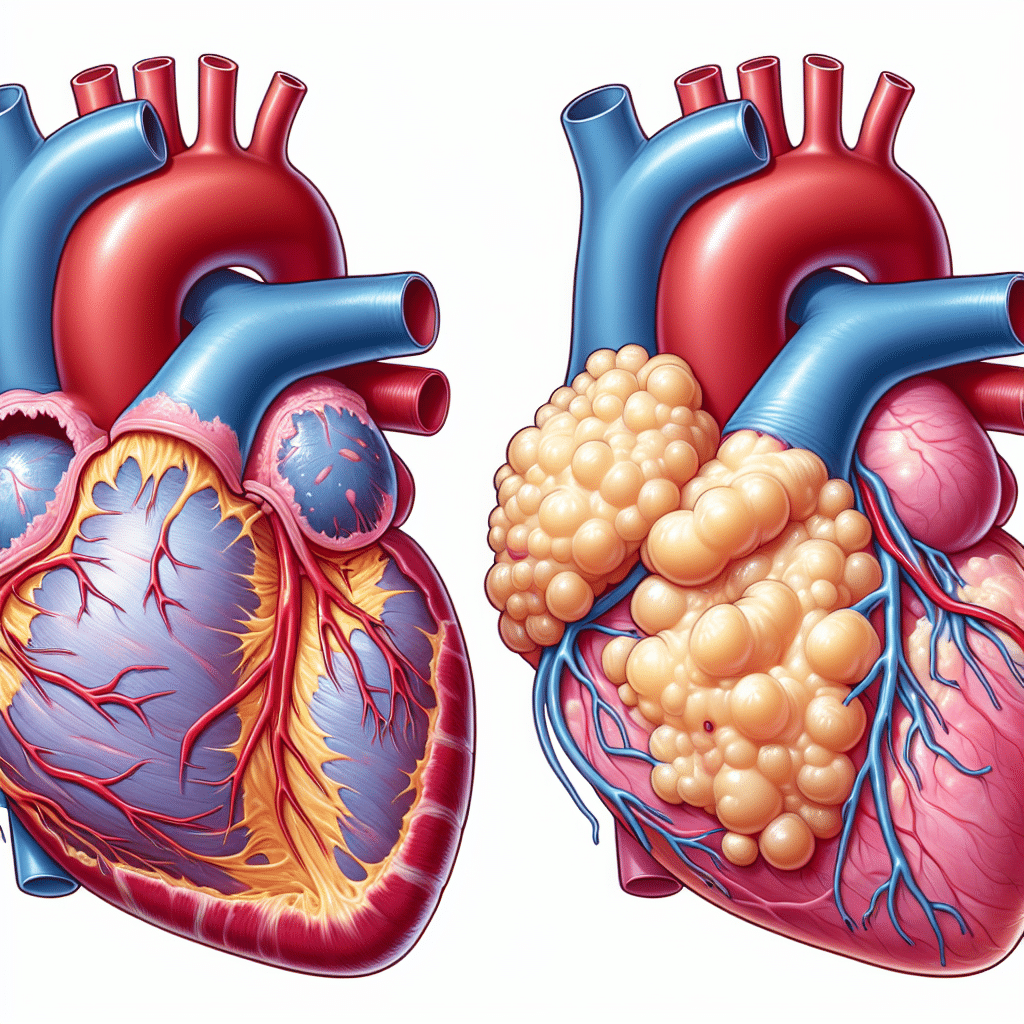
Purulent pericarditis is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition characterized by the accumulation of pus in the pericardial cavity, which surrounds the heart. This condition usually results from an infection, often bacterial, and can lead to severe cardiac complications if left untreated. Symptoms may include chest pain, fever, difficulty breathing, and malaise. Prompt medical intervention is crucial to effectively manage this condition, as it can progress rapidly and require procedures such as pericardiocentesis or surgery to drain the infected fluid. Understanding the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for purulent pericarditis is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients. This article delves into these relevant aspects and more to provide a comprehensive overview.
Understanding Purulent Pericarditis
Purulent pericarditis is often categorized as an acute inflammatory response of the pericardium—an important fibroelastic sac enclosing the heart. Unlike conventional pericarditis, which may arise from viral infections or other non-infectious causes, purulent pericarditis is strictly linked to pathogens, necessitating urgent medical attention.
Causes of Purulent Pericarditis
The primary causes of purulent pericarditis stem from infectious agents such as bacteria, fungi, and, in rare instances, parasites. The most common bacterial culprit is Staphylococcus aureus, followed by Streptococcus and Escherichia coli. In immunocompromised patients, other organisms—including Klebsiella and Mycobacterium tuberculosis—may be implicated.
- Bacterial Infection: Often follows a secondary infection like pneumonia or infective endocarditis.
- Post-Surgical Complications: Surgical procedures involving the heart—such as cardiac surgery or catheterization—can introduce bacteria.
- Direct Spread: Infection may also spread to the pericardium from adjacent structures, such as the lungs.
Symptoms of Purulent Pericarditis
Identifying purulent pericarditis early is critical. Common symptoms include:
- Chest Pain: Often a sharp, stabbing pain worsened by deep breathing or coughing.
- Fever and Chills: Indicative of an underlying infection.
- Dyspnea: Difficulty breathing due to fluid accumulation around the heart.
- Malaise: General feeling of discomfort or unease.
Patients may also exhibit signs of systemic infection, such as tachycardia and hypotension, which can indicate a severe state of illness.
Diagnosis of Purulent Pericarditis
Diagnosing purulent pericarditis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging studies, and laboratory tests.
- Medical History: Investigating prior infections, surgical history, and symptom duration.
- Physical Examination: Notable findings may include a pericardial rub during auscultation.
- Imaging: Echocardiography is the primary imaging technique used to visualize fluid in the pericardial space. CT scans and MRI can provide additional insights.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood cultures, complete blood counts (CBC), and inflammatory markers (e.g., C-reactive protein) help in the assessment.
Treatment Options for Purulent Pericarditis
Treatment for purulent pericarditis focuses on addressing the underlying infection and relieving symptoms. Management strategies include:
- Antibiotic Therapy: Initiating broad-spectrum antibiotics while awaiting culture results, followed by targeted therapy based on sensitivity.
- Pericardiocentesis: This procedure involves the aspiration of purulent fluid to relieve pressure and confirm the diagnosis through laboratory analysis.
- Surgeries: In more severe cases, surgical intervention like pericardiectomy may be necessary to prevent recurrence.
Prognosis and Complications
The prognosis of purulent pericarditis largely depends on the timely initiation of treatment. If promptly diagnosed and managed, the mortality rate can be significantly lowered. However, complications may arise, such as:
- Cardiac Tamponade: This life-threatening condition may occur due to rapid fluid accumulation.
- Chronic Pericarditis: In some cases, the condition may evolve from acute to chronic, necessitating long-term management.
- Recurrence: Persistent infections may lead to further episodes if not adequately treated.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the early signs of purulent pericarditis?
Early signs include chest pain that worsens with breathing, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing.
How is purulent pericarditis treated?
Treatment typically involves the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, pericardiocentesis for fluid drainage, and in some cases, surgery to prevent recurrence.
Can purulent pericarditis be prevented?
While it may not be entirely preventable, maintaining good overall health, prompt treatment of infections, and careful monitoring in high-risk patients can lower the risk.
Is purulent pericarditis contagious?
No, purulent pericarditis itself is not contagious. However, the infections leading to it may spread by direct contact or through respiratory droplets, depending on the causative organism.
Conclusion
Understanding purulent pericarditis is vital for recognition and prompt action. Given its potential to escalate rapidly to serious complications, being aware of symptoms and seeking immediate medical care is crucial. Ongoing research and advancements in medical science continue to enhance treatment protocols, promising better outcomes for affected individuals.