Introduction
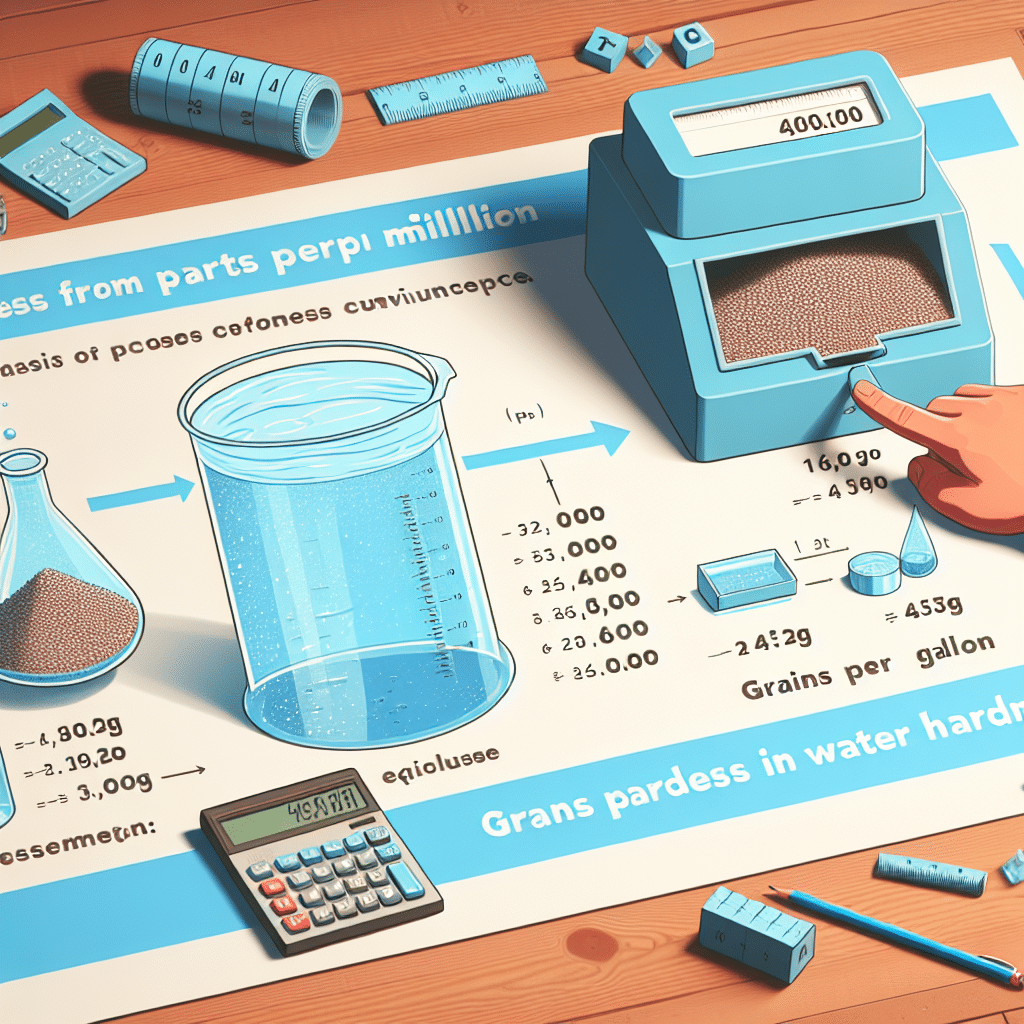
Understanding water hardness is crucial for many applications, from household use to industrial processes. Water hardness is often measured in parts per million (ppm) or grains per gallon (gpg). Specifically, when discussing 400 ppm hardness, it translates to approximately 23.4 gpg. This means that a water sample containing 400 ppm of hardness would have around 23.4 grains of hardness minerals per gallon of water. Such levels of hardness can affect various aspects of water usability, including plumbing systems, soap effectiveness, and appliance longevity. Recognizing this conversion and the implications of hardness levels is essential for anyone managing water quality.
Understanding Water Hardness
Water hardness is primarily due to the presence of calcium and magnesium ions. These minerals come from natural sources such as limestone and gypsum, often dissolving into water as it moves through soil and rock formations. Water hardness can influence everything from municipal water treatment processes to user comfort and appliance maintenance.
Measuring Water Hardness
Hardness can be quantified in several units. The most common measurements include:
- Parts Per Million (ppm): This unit represents the number of milligrams of hardness minerals per liter of water.
- Grains Per Gallon (gpg): This measurement shows the weight of hardness minerals per gallon. One grain is approximately 64.8 milligrams.
The conversion between these units is essential for understanding the water’s suitability for various applications.
Conversion from ppm to gpg
The formula to convert ppm to gpg is straightforward. To convert the hardness from ppm to grains per gallon:
Grains per gallon (gpg) = ppm × 0.0584
Thus, for water with 400 ppm hardness:
400 ppm × 0.0584 = 23.4 gpg.
This conversion helps in understanding the impact of water hardness on household appliances and plumbing systems.
The Impact of 400 ppm Hardness
Effects on Households
Water with a hardness measurement of 400 ppm can lead to several household issues. Soap and detergents do not lather as effectively in hard water, necessitating larger quantities for cleaning tasks. Over time, mineral deposits can accumulate in pipes and appliances, leading to costly repairs and reduced lifespan. Hard water may also affect skin and hair, leading to dryness and irritation for some users.
Effects on Appliances
Hard water can significantly affect the efficiency and lifespan of household appliances like water heaters, dishwashers, and washing machines. The minerals can cause scale buildup on heating elements, reducing efficiency and leading to premature failures. Regular descaling treatments may be necessary to maintain performance levels.
Effects on Municipal Water Supply
For municipal water supply systems, consistent high levels of hardness can complicate treatment processes. Water softening methods, such as ion exchange or lime softening, may be employed to manage hardness and ensure safe and effective water for community use.
Water Softening Methods
Ion Exchange Systems
One of the most common methods to soften water is using ion exchange systems. This technology replaces calcium and magnesium ions with sodium or potassium ions, effectively reducing hardness levels. Households often install these systems to improve water quality for everyday use.
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis is another method that can effectively remove hardness minerals. By forcing water through a semi-permeable membrane, it filters out impurities, including calcium and magnesium, achieving soft water for consumption and use.
Sequestration
Sequestration involves using chemicals such as polyphosphates to bind hardness minerals, preventing them from precipitating and forming scale. This method is effective in situations where hardness levels are significant, particularly in commercial applications.
FAQ
1. What does 400 ppm stand for?
400 ppm (parts per million) represents the concentration of hardness minerals (primarily calcium and magnesium) in water, signifying how many milligrams of these minerals are present in one liter of water.
2. How does 400 ppm hardness affect daily water use?
At 400 ppm, soap efficiency decreases, leading to the use of more product for cleaning tasks, and can result in buildup in plumbing and appliances, impacting their longevity and efficiency.
3. What is the equivalent of 400 ppm in other hardness measurements?
400 ppm translates to approximately 23.4 grains per gallon (gpg), which helps in comparing hardness levels across different measurement systems.
4. How can I determine the hardness of my water?
You can test water hardness using test strips or kits available at local hardware stores or through your water utility provider. Regular testing can provide crucial data for managing water quality.
Conclusion
Recognizing water hardness levels, especially at a concentration of 400 ppm, is imperative for both households and industries. Understanding how to measure, interpret, and manage hardness can lead to better decision-making regarding water treatment and usage. Additionally, employing effective water softening methods can mitigate potential problems associated with high hardness, ensuring that water remains a valuable resource.