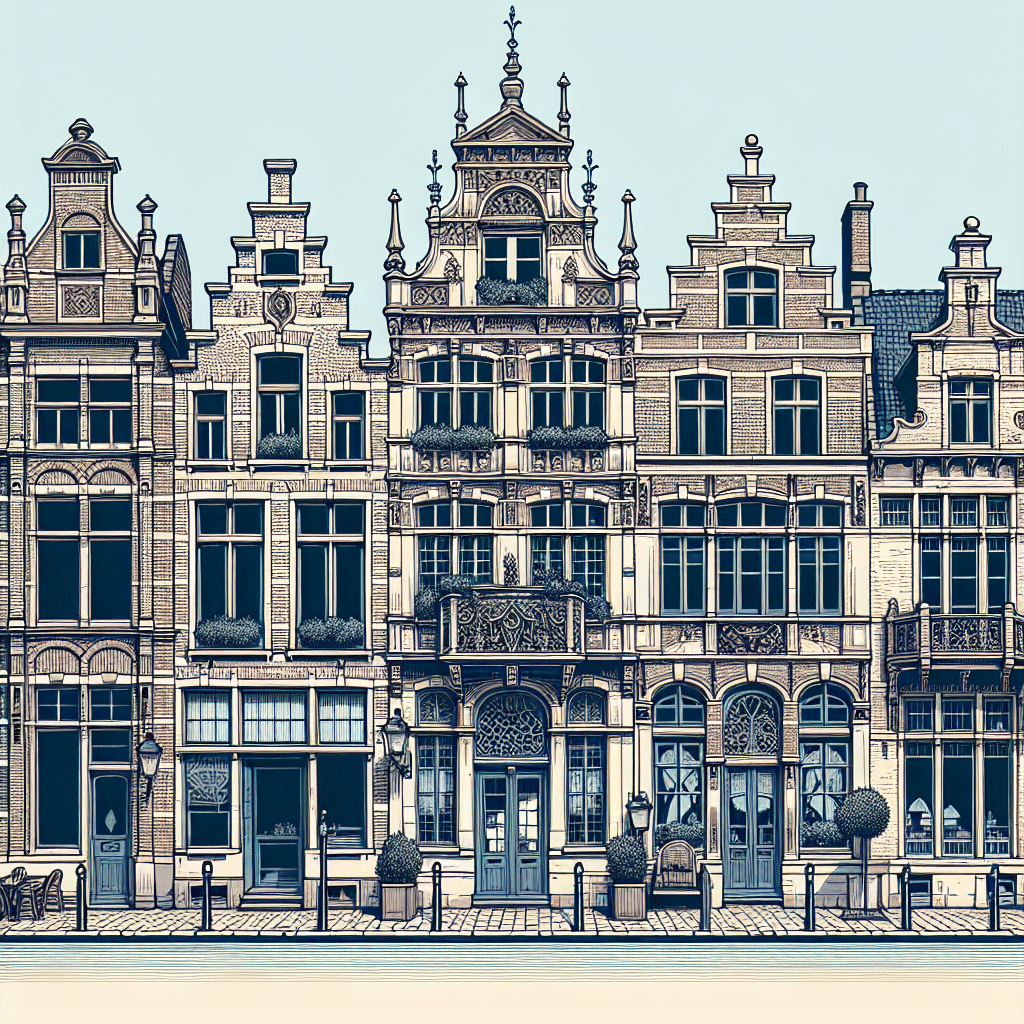
A Belgian in architecture typically refers to a distinctive style or design element originating from Belgium that emphasizes clean lines, functionality, and often an integration with nature. This architectural approach showcases a blend of traditional and modern aesthetics, characterized by the use of natural materials like brick, stone, and wood. Belgian architecture also prioritizes spacious interiors and ample natural light, creating warm and inviting environments. The style is heavily influenced by the country’s rich cultural heritage, and there are various notable architects and movements that have contributed to what is known as Belgian architecture today, including influences from Art Nouveau to contemporary designs. Thus, a Belgian in architecture can embody a diversity of styles, but always with a focus on blending craftsmanship with innovative design.
Understanding Belgian Architecture
Belgian architecture is celebrated not only in its historical context but also for its contemporary contributions to global architecture. It reflects a unique mindset that combines regional character with progressive ideas. To appreciate what constitutes a “Belgian” in architecture, one must consider various factors including historical influences, notable architects, regional styles, and key characteristics that define this architectural identity.
Historical Context
The foundation of Belgian architecture can be traced back to several historical movements and periods. From the Gothic cathedrals of the Middle Ages to the Renaissance palaces, the architectural landscape of Belgium has evolved significantly. The Art Nouveau movement in the late 19th and early 20th centuries profoundly influenced Belgian architecture. Prominent figures like Victor Horta and Paul Hankar championed this style, blending functionality with organic forms and intricate decorative detailing, which are hallmarks of Belgian design.
Key Architectural Movements in Belgium
1. Gothic Architecture
This style dominated from the 12th to the 16th centuries, with notable examples such as the Cathedral of Our Lady in Antwerp and the Grand Place in Brussels. Gothic features include pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses, which accentuated height and light within these structures.
2. Renaissance Architecture
In the 16th century, the Renaissance period introduced symmetrical designs and classical elements. Structures during this time were marked by grand façades and elegant proportions. Key examples include the Town Hall in Brussels, which reflects the grandeur of Renaissance ideals.
3. Art Nouveau
This late 19th to early 20th-century movement is best exemplified in Belgium by architects such as Horta. Art Nouveau architecture utilizes flowing lines and natural forms, often incorporating decorative motifs that celebrate nature, marking a departure from rigid architectural conventions.
4. Modernism
Advancing into the 20th century, modern architecture emerged, emphasizing minimalism, functionalism, and the use of new materials. The contributions of Belgian architects like Marcel Leborgne and the popularity of industrial-style buildings have left a notable mark.
Distinct Characteristics of Belgian Architecture
Understanding what makes Belgian architecture unique involves recognizing its specific traits. These characteristics include:
1. Use of Natural Materials
Belgian architecture often employs materials such as brick, stone, and timber that not only provide structural integrity but also blend harmoniously with the environment. This practice enhances the aesthetic appeal and durability of the designs.
2. Integration with Nature
A strong connection to the natural landscape is a hallmark of Belgian design. Many buildings are strategically positioned to maximize views and light, with large windows and open spaces that invite nature indoors.
3. Minimalism and Simplicity
While historically rich, contemporary Belgian architecture often favors simplicity. Clean lines, neutral color palettes, and functional layouts are common, reflecting a modern ethos that values innovation over ornamentation.
4. Spacious Interiors
Interiors in Belgian homes are typically airy and roomy, facilitating a flow of movement and light. Open floor plans are frequently utilized to create a sense of spaciousness and comfort.
Notable Architects and their Contributions
1. Victor Horta
Horta is renowned for being a founding figure of the Art Nouveau movement, with remarkable works like the Hôtel Tassel and the Maison du Peuple. His innovative use of space and detail set the foundation for modernist principles in architecture.
2. Paul Hankar
Another prominent figure, Hankar, integrated the ideals of Art Nouveau into public and private buildings, emphasizing a decorative, yet functional approach. His works demonstrate the fluidity of Art Nouveau in everyday architecture.
3. Marcel Leborgne
Leborgne contributed significantly to mid-century modern architecture, moving away from historical styles to embrace contemporary forms. His legacy includes the influential use of modern materials and techniques in design.
Contemporary Belgian Architecture
In recent years, Belgian architects have garnered international acclaim for innovative contributions, often exploring sustainability and modern aesthetics. Architects such as Rem Koolhaas and Vincent Callebaut are examples of how Belgian architects continue to lead in the evolution of architectural thought. Their designs frequently blend technology with environmental awareness, showcasing the future direction of architecture in the region.
Challenges and Future Directions
As urbanization and climate challenges escalate, Belgian architecture faces pressing demands for sustainability and adaptability. Architects are called to strike a balance between aesthetics and environmental responsibility, integrating smart technologies and eco-friendly practices into their designs.
FAQ
What defines Belgian architecture?
Belgian architecture is defined by its historical influences, use of natural materials, clean designs, and a strong emphasis on integrating spaces with nature. It evolves from various movements, particularly Gothic, Renaissance, and Art Nouveau.
How does Belgian architecture differ from other European styles?
While sharing some common roots with other European styles, Belgian architecture emphasizes a blend of tradition and modernity with a focus on functionality and minimalism. This sets it apart from more ornate styles found in other regions.
Who are the most influential Belgian architects?
Victor Horta and Paul Hankar are among the most influential architects in Belgian history, especially known for their roles in the Art Nouveau movement. Contemporary figures like Rem Koolhaas also play a significant role in shaping modern architecture.
What are the future trends in Belgian architecture?
Future trends in Belgian architecture are leaning towards sustainability, innovative urban designs, and smart architectural solutions that address climate change while enhancing quality of life in urban areas.
Conclusion
Belgian architecture is a testament to a rich cultural history that resonates through its modern applications. The blend of traditional craftsmanship and innovative techniques continues to define what is a “Belgian” in the architectural landscape, making it not only unique but also relevant as it addresses contemporary and future challenges. Understanding this evolution provides insights into the broader context of architecture in Europe and beyond.