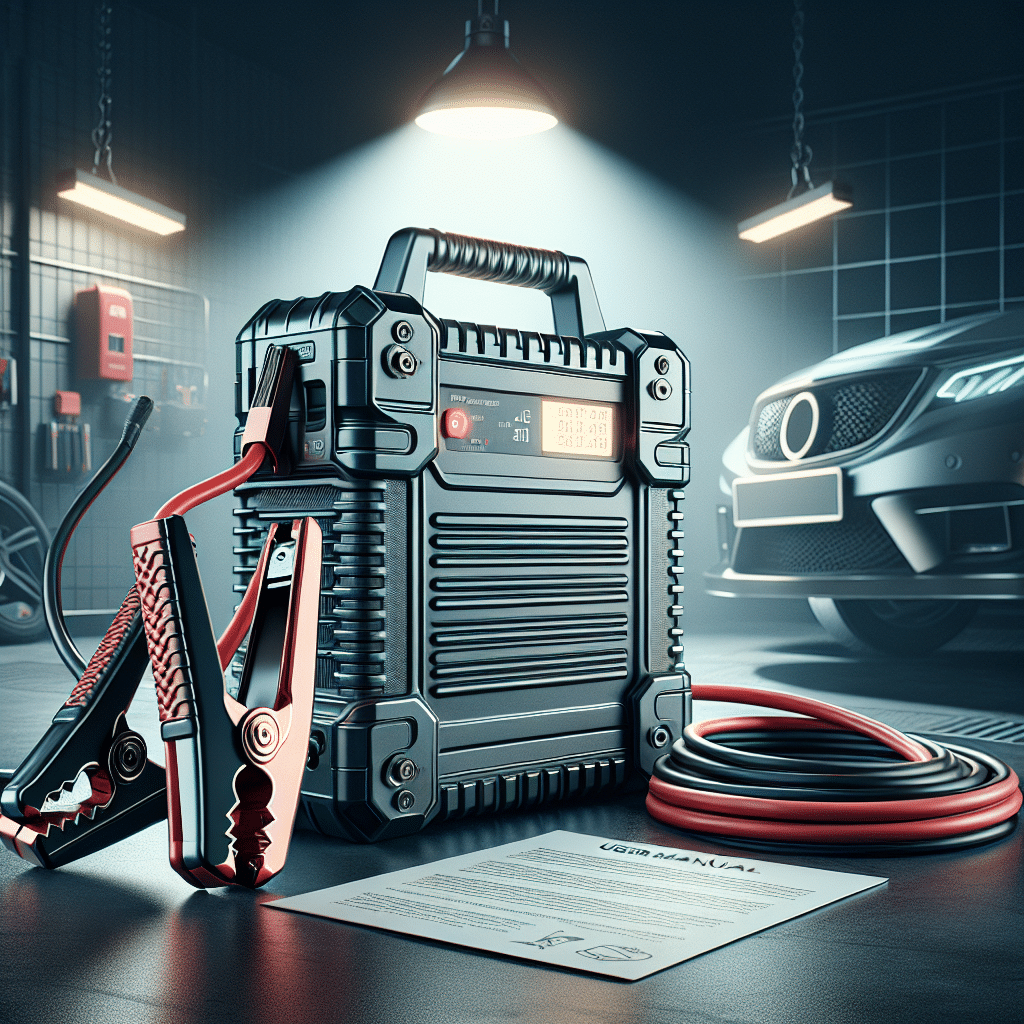
A good power for a jump starter typically ranges between 400 to 800 peak amps for standard vehicles. For larger engines or trucks, look for jump starters that deliver 1000 peak amps or more. This ensures that the jump starter has sufficient power to start even the most challenging engines, especially in cold weather. Understanding the specifications, including the difference between peak and cranking amps, is crucial. Peak amps indicate the maximum burst of power available for a short time, while cranking amps measure the sustained power over a longer duration. Therefore, choosing a jump starter with the right power rating is essential for reliability and performance during emergencies.
Understanding Jump Starter Power Ratings
When you’re stranded with a dead battery, having the right jump starter can make all the difference. But what constitutes “good power” in a jump starter? Understanding the power specifications can help you select the best device for your needs.
Key Power Metrics: Peak Amps vs. Cranking Amps
Two primary metrics define the power capabilities of a jump starter: peak amps and cranking amps. Both are essential for understanding how effective a jumper pack will be in real-world scenarios.
- Peak Amps: This metric indicates the maximum power delivered by the jump starter for a brief moment, typically for a few seconds. It is crucial for providing the initial boost needed to turn over a dead battery.
- Cranking Amps: In contrast, cranking amps measure the power output over a more extended period (usually 30 seconds). This is important during colder temperatures or when handling larger engines that may require more sustained power to start.
What is a Good Power Rating for Your Needs?
The appropriate power rating largely depends on the type of vehicle. Here’s a rough guideline:
- For cars and small SUVs: Aim for a jump starter with a minimum of 400-600 peak amps.
- For larger vehicles, including trucks and SUVs with larger engines: Look for at least 800-1000 peak amps.
- For diesel engines or high-performance vehicles: Consider a jump starter with 1000 peak amps or more.
Battery Technology in Jump Starters
When evaluating jump starters, the type of battery technology used is also critical. Common types include:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Traditionally used in jump starters, they are effective but generally heavier and less portable.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: These are lighter, have a higher energy density, and typically offer more cycles than lead-acid batteries. They can be convenient for everyday carry.
Additional Factors to Consider
Besides peak and cranking amps, there are additional factors that influence the effectiveness of a jump starter:
1. Size and Portability
Choose a jump starter that you can conveniently store in your vehicle. Compact models with high power outputs are ideal for practicality.
2. Safety Features
Look for models equipped with safety features such as spark-proof technology and reverse polarity protection to prevent potential mishaps during use.
3. Additional Functions
Many modern jump starters come with additional functionalities, such as USB ports for charging devices, built-in flashlights for emergencies, and air compressors. These features can add significant value.
4. Brand Reputation and Reviews
Consider purchasing a jump starter from reputable brands known for reliability. Reading customer reviews can also provide insight into the product’s performance in real-world situations.
Real-World Examples and Expert Opinions
Several popular jump starters on the market serve as excellent examples of what constitutes good power in this device category:
- NOCO Boost Plus GB40: With 1000 peak amps, this lithium-ion jump starter is suitable for a wide range of vehicles, including cars and trucks, making it a popular choice among users.
- DBPOWER 800A Portable Car Jump Starter: This model features 800 peak amps and offers additional functions like USB ports, showing how practicality and good power can coexist.
- Clore Automotive Jump-N-Carry JNC660: A heavyweight in the jumper market, it boasts 1700 peak amps, making it an excellent option for serious practitioners, such as mechanics.
FAQ: Common Questions about Jump Starter Power
1. Can I use a jump starter on any car?
Most jump starters are versatile enough to work with various vehicle types, but always check the power output and consult your vehicle’s manual to ensure compatibility.
2. How long does a jump starter last?
The lifespan of a jump starter depends on usage and care. Regular maintenance and proper charging can keep a unit functional for several years. Lithium-ion models often last longer than traditional lead-acid models.
3. Is it safe to use a used jump starter?
While it can be safe to use a secondhand jump starter, ensure that it has been well-maintained. Check for any visible signs of wear and perform a function test before relying on it in an emergency.
4. How do I maintain my jump starter?
For optimal performance, charge your jump starter regularly, store it in a cool, dry place, and follow manufacturer guidelines for use and maintenance.
5. Can a jump starter charge my car battery?
No, jump starters are primarily meant for starting cars with dead batteries. However, some models feature charging ports for powering electronic devices.
Final Thoughts on Jump Starter Power
In conclusion, selecting a jump starter with appropriate power specifications is vital for reliable vehicle starts. By understanding peak and cranking amps, considering battery technology, and evaluating additional features, you can make an informed decision. Remember always to prioritize safety and usability, ensuring that you are prepared for any roadside emergency.