What is a Mill?
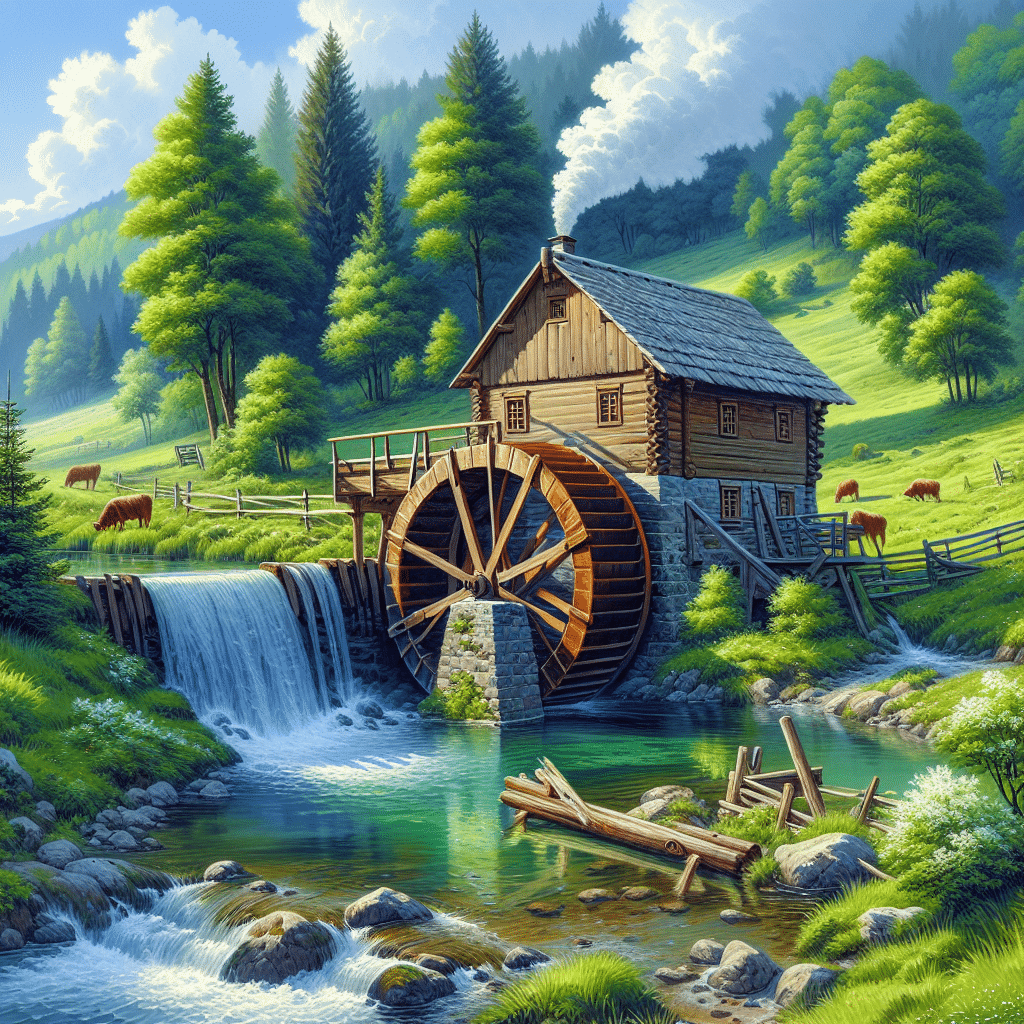
A mill is a facility or machine used for grinding, crushing, or processing material, typically grain or minerals, to produce a finer product. Originating from ancient times, mills serve essential functions in agriculture and manufacturing, transitioning from water-powered systems in the early days to modern electric and automated machines. A grain mill, for instance, converts whole grains into flour, while a sawmill processes timber into lumber. The invention of the mill significantly revolutionized food production, craftsmanship, and various industries, making it a vital component of economic development.
Types of Mills
1. Grain Mills
Grain mills are designed specifically for milling grains. These can range from small domestic models to large commercial operations. They typically use rollers or stones to break down grains into flour or meal. Various types of grain mills include:
- Stone Mills: Use stones to grind grains, providing a traditional method of milling. They tend to retain more nutrients but also require more time.
- Roller Mills: Utilize cylindrical rollers to crush grain, predominantly used in commercial flour production for their efficiency and speed.
- Hammer Mills: Employ a high-speed rotating blade to shred the grain, suitable for feed production.
2. Saw Mills
Saw mills are dedicated to processing timber. They convert logs into dimensional lumber, siding, and other wood products. The sawmill industry plays a crucial role in providing raw materials for construction and furniture manufacturing.
3. Textile Mills
Textile mills manufacture fabric and textiles from natural or synthetic fibers. They use various methods such as weaving, knitting, and felting to produce finished textile products.
4. Other Specialized Mills
Mills are also used in other industries, including:
- Cement Mills: Grind clinker into powder, forming the basis of cement.
- Plastic Mills: Break down plastics for recycling or processing.
The History of Mills
The history of mills dates back thousands of years to ancient civilizations, where they utilized watermills and windmills. The watermill harnessed water flow to turn a wheel, powering the grinding mechanism, while the windmill used wind energy for similar purposes. The introduction of these power sources revolutionized agricultural practices and food production.
With the industrial revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries, mills transitioned from small, water- or wind-powered structures to large industrial plants capable of producing goods at unprecedented scales. This shift enabled mass production, altering economies globally.
How Mills Operate
The operation of mills can vary significantly based on the type of mill and materials processed. However, most share common operational principles:
- Raw Material Input: The process begins with the introduction of raw materials into the mill. This can include grains, logs, or other raw commodities.
- Grinding Mechanism: The raw materials are subjected to grinding or crushing utilizing mechanical forces such as pressure, impact, or shear force.
- Separation and Classification: Post milling, the product often undergoes separation to achieve desired consistency and quality, using techniques like screening or air classification.
- Output: The final product, whether flour, lumber, or fabric, is collected and prepared for packaging or further processing.
The Importance of Mills in Modern Society
Mills play a crucial role in various sectors, impacting daily life and the economy. Some key points include:
- Food Production: Grain mills are fundamental for producing flour, impacting bread, pasta, and many processed foods consumed daily.
- Construction Materials: Sawmills are vital for producing lumber used in residential and commercial construction, supplying essential building materials.
- Economic Development: Mills contribute significantly to local and national economies by providing jobs and fostering industries.
- Innovation: Modern mills often incorporate advanced technology, allowing for greater efficiency and sustainability, such as reducing waste and energy consumption.
Environmental Considerations
While mills are essential for production, they also impact the environment. Key considerations include:
- Resource Consumption: The milling process requires significant resources, including water and energy, leading to potential sustainability challenges.
- Waste Generation: Mills can produce considerable waste products that must be managed responsibly to mitigate environmental harm.
- Carbon Footprint: Energy consumption in mills contributes to greenhouse gas emissions; thus, adopting cleaner technologies can minimize environmental impacts.
Future Trends in Milling
The milling industry is continually evolving. Current trends shaping the future include:
- Automation: Many mills are adopting automation and smart technologies for improved efficiency and consistency in production.
- Sustainability Practices: Increased focus on using renewable energy, reducing waste, and sourcing raw materials responsibly.
- Health and Nutrition: A rising consumer interest in whole grains and healthier product options is influencing grain mill operations to produce more nutritious products.
FAQ
What is the primary function of a mill?
The primary function of a mill is to grind or crush raw materials into finer substances, such as converting grains into flour or logs into lumber.
What types of products can be produced by mills?
Mills produce a wide range of products, including flour, lumber, textiles, and cement, based on the type of mill.
How do modern mills differ from traditional mills?
Modern mills often employ advanced technology and automation, enabling higher efficiency, consistency, and precision compared to traditional, manual methods.
What environmental practices are mills adopting?
Mills are implementing sustainable practices such as reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and using eco-friendly materials in their operations.
Conclusion
Mills have significantly shaped the course of human development and continue to be crucial in producing essential goods. By understanding the diverse types of mills, their operations, and their impact on society, we gain insight into their integral role in modern economies. Embracing sustainable practices and advancing technologies will help ensure that mills remain efficient and environmentally responsible in the future.