Introduction
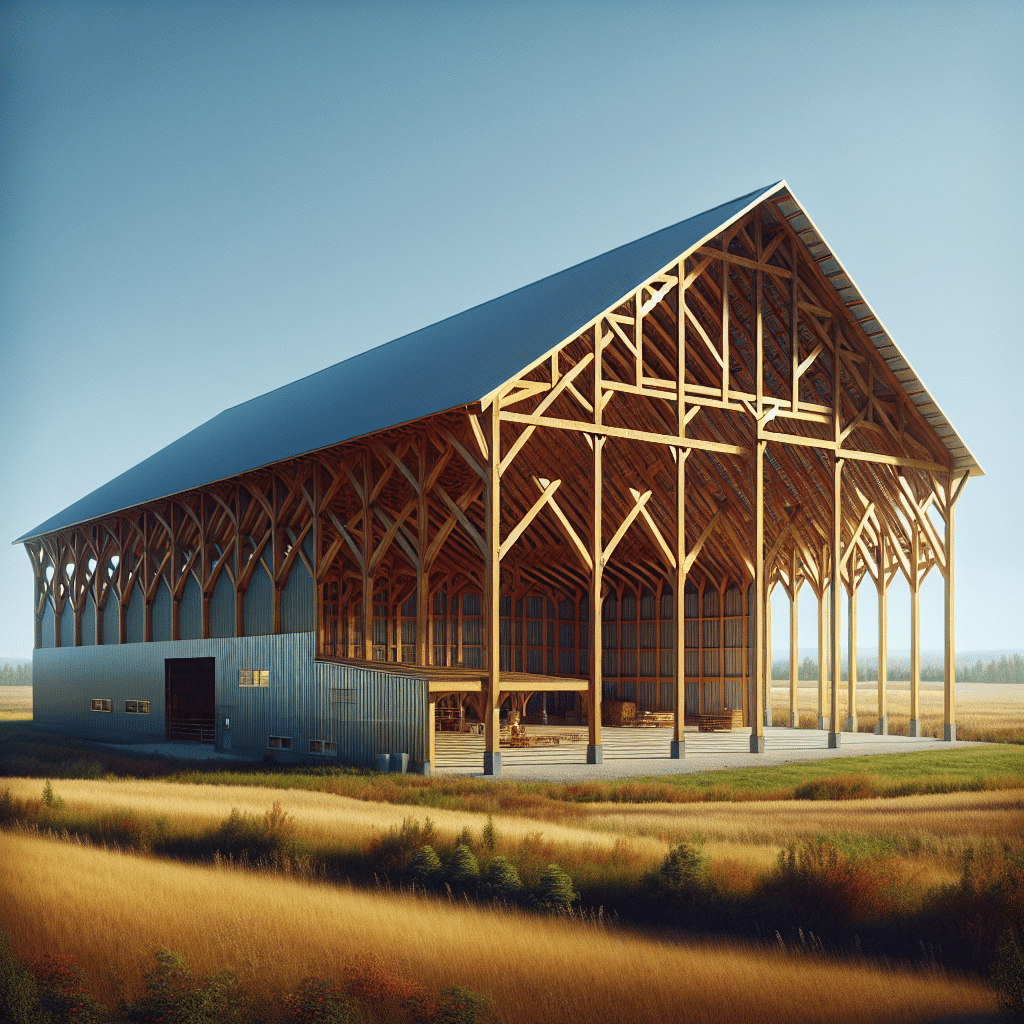
A pole barn is a type of structure commonly used in agriculture, storage, and many other applications, characterized by its distinct pole-frame construction. Unlike traditional buildings that use a concrete foundation and load-bearing walls, a pole barn is built using large poles or posts anchored in the ground, which form the skeletal frame of the building. This design allows for open space and flexibility in interior configuration, making pole barns particularly suitable for storage, workshops, and agricultural purposes. Additionally, they are often more economical to construct and require less building material than conventional structures. As such, they have gained popularity across the United States for both commercial and residential purposes.
Understanding Pole Barns
What is a Pole Barn?
A pole barn utilizes a post-frame construction technique, where vertical posts or poles serve as the primary support structure. These poles are typically embedded in the ground or set in concrete, providing a robust foundation without the need for a full basement or continuous concrete foundation.
History and Evolution
The concept of pole barns dates back to the early 20th century, primarily used in rural areas for agricultural purposes such as housing livestock, storing equipment, and sheltering crops. Over the years, the design has evolved, incorporating a range of materials such as metal roofing and siding, making them versatile and resilient against various weather conditions.
Key Features of Pole Barns
- Open Space Design: The absence of load-bearing walls allows for customizable interior spaces, which can be adjusted based on user needs.
- Cost-Effective: Pole barns are generally less expensive to build compared to traditional structures, given their simpler design and fewer materials.
- Speed of Construction: These buildings can often be erected more quickly, making them ideal for urgent needs.
- Low Maintenance: Many pole barns utilize durable materials that require less upkeep over time.
Construction Process
Site Preparation
Beginning with site preparation, the chosen location should be evaluated for drainage, accessibility, and zoning regulations. Grading might be necessary to ensure a level foundation.
Setting the Posts
The poles are typically made of treated wood and are set in concrete footings, usually spaced apart to accommodate walls or other structures. The depth and spacing will depend on the desired size of the barn and local building codes.
Framing and Roofing
Once the posts are secured, horizontal girts are installed between them, creating a framework where walls and roofs can be attached. Roofing materials can vary widely, from metal panels to shingles, depending on budget and aesthetic preferences.
Finishing Touches
The final stages may include installing doors, insulation, electrical systems, and any interior divisions that are desired. Many owners opt for large sliding doors or roll-up doors for easy access.
Applications of Pole Barns
Agricultural Use
Originally designed for farming, pole barns remain a choice among agricultural communities. They house livestock, store feed, and serve as equipment garages.
Commercial Use
Many businesses utilize pole barns for storage and workshop facilities due to their spacious design and economic advantages. They’re also used in retail, particularly for garden centers and pet supply stores.
Residential Use
In recent years, the use of pole barns for residential purposes has surged. Many homeowners create multipurpose spaces that can include garages, guesthouses, or even homes. Their design flexibility allows for unique homes that can be tailored to individual preferences.
Pros and Cons of Pole Barns
Advantages
- Cost-effectiveness
- Quick construction times
- Flexible interior space
- Adaptable for various uses
- Durability and low maintenance
Disadvantages
- Potential zoning restrictions
- Limited insulation capabilities compared to traditional homes
- May require additional permits for residential use
Regulatory Considerations
When considering a pole barn, it’s essential to understand local zoning laws and building codes. These regulations can dictate the structure’s size, purpose, and placement on the property. It’s advisable to check with local authorities prior to construction to ensure compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long do pole barns last?
With proper maintenance and care, pole barns can last for several decades, often exceeding 30 years, especially if constructed using treated wood and durable materials.
Can I insulate a pole barn?
Yes, insulation can be added to a pole barn structure, although the process may differ from traditional homes. Options like spray foam, fiberglass, or rigid panels can be employed based on the intended use of the barn.
Are pole barns considered permanent structures?
Generally, pole barns are categorized as permanent structures due to their foundation and construction methods, though their classification can depend on local laws and definitions.
What is the cost of building a pole barn?
The cost varies widely based on size, materials, and location. On average, constructing a pole barn can range from $15 to $30 per square foot, although more complex designs may increase this cost.
Conclusion
In summary, pole barns offer a versatile, economical solution for a wide range of storage and structural needs, whether for agriculture, business, or residential use. Their unique construction methods and adaptability make them a popular choice in the United States, appealing to those looking for a functional, cost-effective building solution. By understanding the elements involved in constructing and maintaining a pole barn, you can make informed decisions that align with your specific requirements.