Introduction
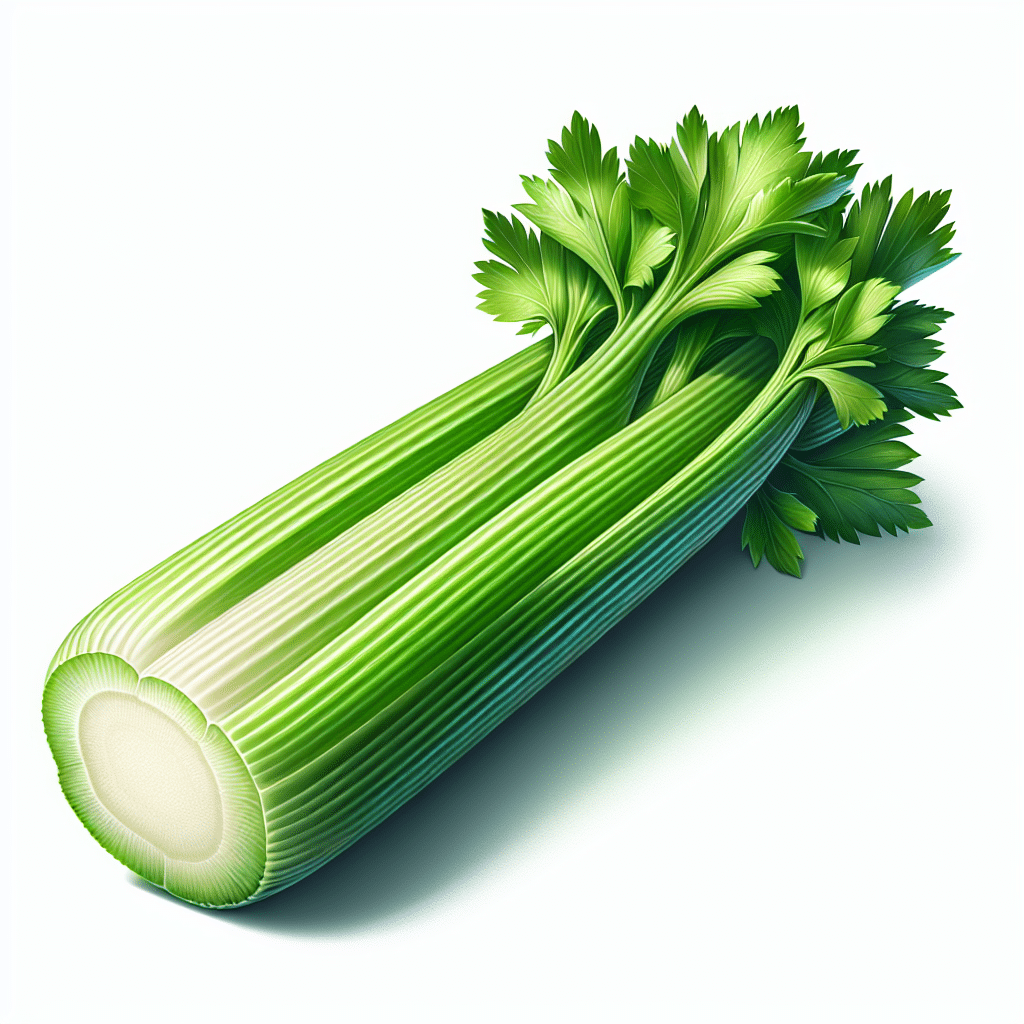
A stalk of celery refers to the long, fibrous stem of the celery plant (Apium graveolens), a member of the Apiaceae family. Commonly recognized for its crisp texture and pale green color, celery is not only a popular vegetable in salads and snacks but also a staple in various culinary dishes, adding both flavor and nutrition. In terms of anatomy, a single stalk is comprised of tightly packed rib-like sections, referred to as ribs, which are attached to a central core. Celery is known for its low-calorie content, making it a favored choice for health-conscious individuals. It is rich in vitamins, particularly vitamin K, and contains essential minerals such as potassium and folate. Additionally, the vegetable is celebrated for its hydrating qualities, as it consists of about 95% water. This combination of nutritional benefits and culinary versatility makes a stalk of celery an invaluable component of the modern diet.
Understanding Celery
The Celery Plant
Celery is a biennial plant that is cultivated as an annual vegetable. It thrives in temperate climates and is typically grown for its edible leaves, stalks, and seeds. The primary edible component is the stalk, which grows in a rosette formation. The plant can grow up to 1–2 feet tall and features glossy, dark green leaves.
Culinary Uses
In the kitchen, celery serves multiple roles:
- Snacking: Celery sticks are often enjoyed raw with dips such as hummus or peanut butter.
- Flavor Base: Chopped celery is a key ingredient in mirepoix, which forms the flavor base for soups, stews, and sauces.
- Soups and Stews: Celery adds depth of flavor when included in various dishes, particularly in combination with other vegetables.
Nutritional Profile
Vitamins and Minerals
A stalk of celery is surprisingly nutrient-dense despite its low-calorie content. Here are some key nutrients found in celery:
- Vitamin K: Essential for blood clotting and bone health, a single stalk can provide significant daily values.
- Folate: Important for cell division and DNA synthesis, making it vital for pregnant women.
- Potassium: Helps to regulate blood pressure and maintain proper heart function.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that supports immune function and skin health.
Hydration Benefits
Because it consists of approximately 95% water, celery is an excellent hydrating food. Including it in your diet can contribute to overall hydration, particularly in warm climates or after exercise.
Growing Celery
Conditions for Growth
Celery requires specific growing conditions:
- Soil: Prefers well-drained, fertile soil with high organic matter.
- Sunlight: Thrives in full sunlight but can tolerate partial shade.
- Water: Requires consistent moisture; drought can lead to poor stalk development.
Timeframe for Harvesting
Generally, celery takes about 130 to 140 days from seedling to harvest. Once mature, the stalks can be cut individually at the base or harvested entirely.
Health Benefits of Celery
Weight Management
Given its low-calorie count, celery is an excellent addition to a weight management plan. Its high water and fiber content can contribute to a feeling of fullness, reducing overall calorie intake.
Digestive Health
Celery is also known to be a good source of dietary fiber, which aids digestion. Regular consumption can contribute to improved gut health and help prevent constipation.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Certain phytochemicals in celery, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, exhibit anti-inflammatory properties. Studies suggest that these compounds can help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases.
Potential Risks and Considerations
Allergies
While celery is generally safe for most people, it can trigger allergic reactions in some individuals. Symptoms may include itching, swelling, and gastrointestinal distress.
Pesticide Residues
Celery is often listed among the “Dirty Dozen,” a term that refers to fruits and vegetables that are more likely to have pesticide residues. To mitigate this, consider purchasing organic celery or washing it thoroughly before consumption.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a stalk and rib of celery?
A stalk of celery refers to the entire stem, while a rib specifically refers to each individual section that composes the stalk.
2. Can you eat celery leaves?
Yes, celery leaves are edible and can be used as a flavorful garnish or added to salads, soups, and stir-fries.
3. How should I store celery to keep it fresh?
Store celery in the refrigerator, wrapped in aluminum foil or placed in a container filled with water to maintain its crispness.
4. Is celery part of any specific diet?
Yes, celery is often included in numerous diets, such as ketogenic, paleo, and Mediterranean diets, due to its low-calorie and high-fiber nature.
Conclusion
A stalk of celery is much more than a simple vegetable; it is a versatile ingredient that offers significant health benefits and culinary uses. Incorporating celery into your diet can improve overall nutrition and well-being while complementing a wide range of dishes. Whether you enjoy it raw as a snack or as a flavorful addition to your meals, celery’s crisp texture and hydrating properties make it a fantastic choice for anyone looking to enhance their diet.