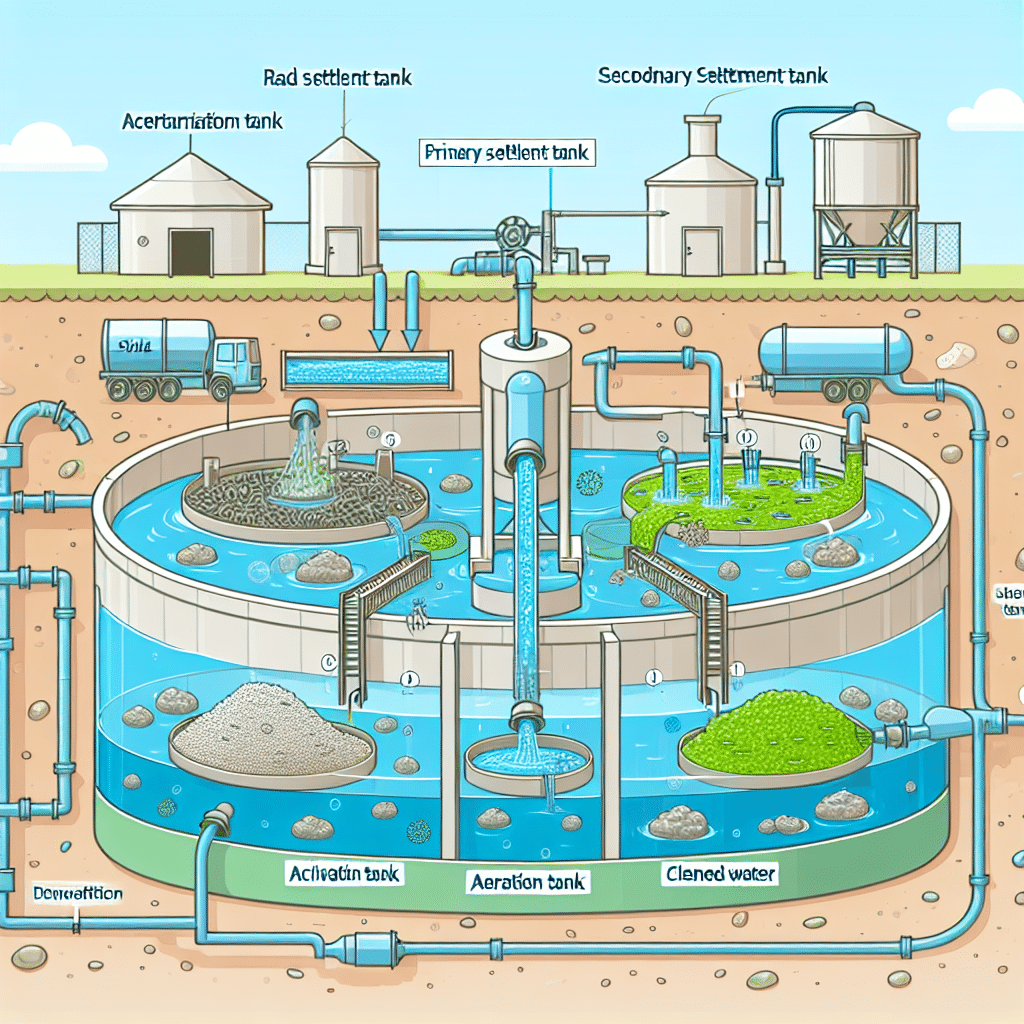
Activated sewage, more commonly referred to as activated sludge, is a biological treatment process used to manage wastewater in treatment plants. This method utilizes microorganisms, specifically bacteria, to break down organic matter in sewage. The activated sludge process involves aerating wastewater to promote the growth of these microorganisms, which consume pollutants and convert them into biomass. The result is cleaner water that can be released into the environment or further treated for reuse. This process is an essential part of modern wastewater management, playing a significant role in reducing the environmental impact of sewage discharge and ensuring public health safety.
Understanding Activated Sewage Treatment
Activated sewage treatment is a critical component of wastewater management systems across the United States. It is characterized by the following key aspects:
1. The Science Behind Activated Sewage
Activated sewage treatment fundamentally relies on the natural biological processes of microorganisms. Bacteria play a pivotal role as they metabolize organic contaminants, converting them into less harmful substances. In this context, the “activated” component refers to the process whereby these bacteria are stimulated through aeration, facilitating their growth and effectiveness.
2. Key Components of the Process
The activated sewage treatment process is comprised of several essential components:
- Influent: This is the incoming sewage that requires treatment and contains organic matter, nutrients, and pollutants.
- Aeration Tank: This chamber allows for the mixing of sewage with a large population of bacteria. Air is injected into the tank, providing oxygen necessary for bacterial metabolism.
- Secondary Clarifier: After aeration, the mixture moves to this tank where the heavier biomass settles out as sludge, separating from the treated water.
- Return Activated Sludge: Some biomass is returned to the aeration tank to maintain a consistent population of bacteria, while excess sludge (waste activated sludge) is removed for further treatment.
3. Phases of the Activated Sludge Process
The activated sewage treatment typically follows these interconnected phases:
- Pre-treatment: Initial screening and grit removal of large and heavy solids from the wastewater.
- Aerobic Respiration: Bacteria consume organic material under aerobic conditions in the aeration tank.
- Settling: In the secondary clarifier, treated water settles, and excess biomass is either recycled or disposed of.
- Post-treatment: Further treatment processes may include disinfection to eliminate pathogens before discharge.
Benefits of Activated Sewage Treatment
The benefits of using the activated sewage treatment method encompass various environmental, economic, and public health aspects:
- Effective Removal of Pollutants: The process efficiently removes organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus, helping achieve regulatory compliance.
- Resource Recovery: The produced biosolids can be used as fertilizers, contributing to sustainability.
- Reduced Impact on Water Sources: By treating wastewater effectively, the process protects aquatic ecosystems and can even enable water reuse initiatives.
Challenges in Activated Sewage Treatment
While activated sewage treatment has numerous advantages, it is not without challenges:
- Operational Complexity: Maintaining optimal conditions for microbial activity can be challenging, requiring skilled personnel and sophisticated monitoring systems.
- Sludge Management: Proper disposal or recycling of excess sludge generated is crucial, as it presents logistical and environmental complexities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring consistent compliance with local and federal regulations is essential for protecting public health and the environment.
Current Trends in Activated Sewage Treatment
Recent advancements in technology and methods have enhanced the effectiveness of activated sewage treatment:
- Process Optimization: Innovations like the use of automation and artificial intelligence are improving operational efficiency and reducing costs.
- Enhanced Nutrient Removal: New techniques are being developed to further optimize the removal of nitrogen and phosphorus, addressing eutrophication issues in receiving waters.
- Decentralized Systems: Smaller, localized treatment facilities are being considered for areas with limited infrastructure, promoting sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What types of sewage are treated with activated sludge?
Activated sludge is primarily used for treating municipal wastewater, including domestic sewage and some industrial wastes. It is effective in degrading organic pollutants found in these wastes.
How does the aeration process work in activated sewage treatment?
The aeration process involves inserting air into the wastewater to mix it with the activated sludge. This provides oxygen, essential for aerobic bacteria to thrive and metabolize organic materials.
What happens to the sludge produced during the treatment process?
Excess sludge produced, referred to as waste activated sludge, is often treated through methods such as anaerobic digestion, composting, or incineration. The remaining biosolids can serve as fertilizers or soil conditioners.
Is activated sewage treatment environmentally sustainable?
Yes, activated sewage treatment is generally considered environmentally sustainable. It minimizes pollution and protects natural water bodies while contributing to resource recovery and efficient waste management.
How often does wastewater need to be treated in activated sewage systems?
Wastewater is typically treated continuously in activated sewage systems, as the flow of influent varies. Treatment facilities are designed to handle fluctuations and ensure consistent water quality.
Conclusion
Activated sewage treatment is a vital component of modern wastewater management, effectively mitigating environmental impacts and safeguarding public health. By harnessing biological processes, this method not only treats sewage but also recycles resources, aligning with sustainability efforts. As technologies continue to evolve, the effectiveness and efficiency of activated sewage processes are expected to improve, ensuring clean water for future generations.