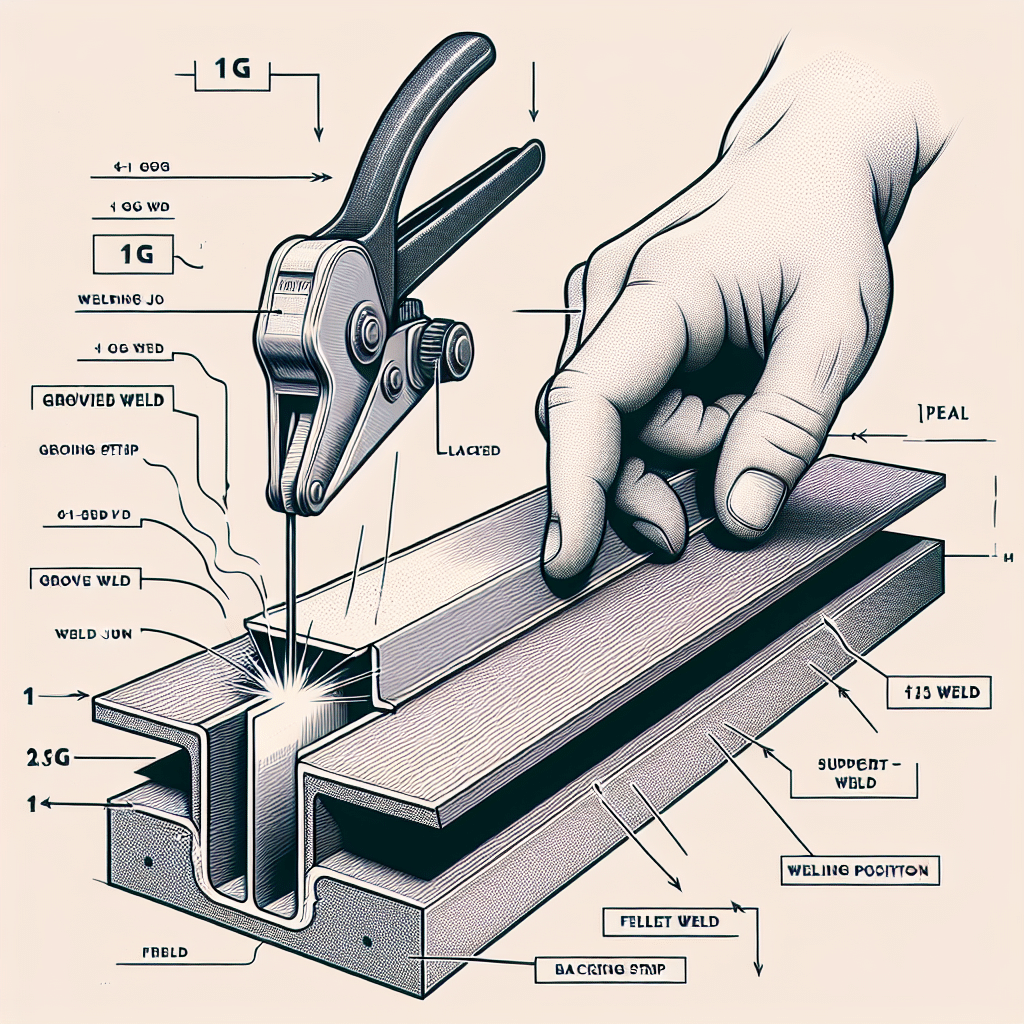
Understanding Backing Strip 1G and 1F
Backing strips, specifically designated as 1G and 1F, serve pivotal roles in various construction and engineering contexts. These strips are predominantly used to provide structural support and enhance the integrity of joints in applications such as concrete, masonry, or composite materials. The designation of 1G typically refers to backing strips designed for general applications, while 1F strips are specifically formulated for fire-resistant materials and environments. Both types serve to enhance the bond strength between materials while also allowing for necessary movement and expansion, critical in maintaining the longevity of structures. The right choice and application of these backing strips can result in improved durability and performance of the overall assembly. This guide delves deeper into the specifications, application techniques, and benefits associated with backing strips 1G and 1F, ensuring you make informed decisions in your projects.
What are Backing Strips?
Backing strips are materials placed behind a joint or seam to provide support and enhance the performance characteristics of sealants or adhesives used in various construction applications. They are critical in ensuring that joints can accommodate movement, reduce voids between materials, and enhance overall joint integrity.
Types of Backing Strips
1G Backing Strips
The “1G” designation typically refers to a general-purpose backing strip that can be used in a variety of applications. These strips are designed to be compatible with different sealants and adhesives, creating a reliable interface for effective bonding. 1G backing strips are often made from materials that provide high compressibility and resilience, which allows for optimal joint performance.
1F Backing Strips
In contrast, “1F” backing strips are specifically engineered for fire-rated applications. These strips are essential when working with materials that need to meet strict fire safety regulations. Made from fire-resistant materials, 1F backing strips help maintain the integrity of a joint during fire exposure, ensuring that the surrounding structures do not suffer catastrophic failure. This makes them critical in commercial buildings, high-rise constructions, or any application where fire safety is a concern.
Key Functions of Backing Strips
- Structural Support: They provide support behind a joint, enhancing the load-bearing capacity.
- Expansion Management: Backing strips allow for thermal expansion and contraction without causing damage to the joint.
- Sealant Efficiency: They create an optimal sealant joint shape, improving adhesion and flexibility.
Applications of Backing Strips
Backing strips are utilized in various applications across different industries. Their proper application is crucial for achieving the desired performance objectives.
Construction and Civil Engineering
In the construction sector, 1G and 1F backing strips are utilized in structural joints, curtain walls, and precast concrete applications. They provide necessary support and enhance the durability of joints under various environmental conditions.
Fire Safety Applications
1F backing strips are critical in applications where fire safety is paramount, including fire-rated walls, doors, and window frames. They help ensure that joints can withstand the intense heat of a fire while maintaining structural integrity for as long as required.
Choosing the Right Backing Strip
Selecting the appropriate backing strip depends on various factors, including the type of materials being used, the specific application, and any regulatory requirements. Here are some considerations:
- Material Compatibility: Ensure that the backing strip is compatible with the sealants or adhesives used.
- Movement Capability: Choose a strip that can accommodate the anticipated movement within the joint.
- Fire Rating: Verify whether your application requires a fire-rated backing strip, especially in commercial constructions.
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation of backing strips is integral for achieving optimal performance. Follow these guidelines:
- Preparation: Clean and prepare the surfaces where the backing strip will be installed.
- Placement: Ensure the backing strip is positioned correctly to support the joint without creating voids.
- Sealing: Apply the sealant according to the manufacturer’s specifications, ensuring even coverage over the strip.
FAQs About Backing Strips 1G and 1F
What materials are backing strips 1G and 1F made from?
Backing strips can be made from various materials, including closed-cell foam, polyethylene, and fire-resistant materials for 1F strips.
Are backing strips necessary for all construction joints?
While not every joint requires backing strips, they are highly recommended for joints that will experience movement or require sealant for water resistance.
Can I use 1G backing strips in fire-rated applications?
1G backing strips are not designed for fire-rated applications. For such scenarios, 1F backing strips should be used to ensure compliance with fire safety standards.
How do I know which size of backing strip to use?
Select the size based on the joint dimensions and the requirements specified for the sealant being used. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for recommended dimensions.
Conclusion
Backing strips 1G and 1F are indispensable components in modern construction and engineering projects. Understanding their distinct properties, applications, and installation techniques can significantly influence the performance and longevity of structural joints. By selecting the appropriate backing strips, you can enhance both the safety and durability of your constructions, ensuring they stand the test of time.