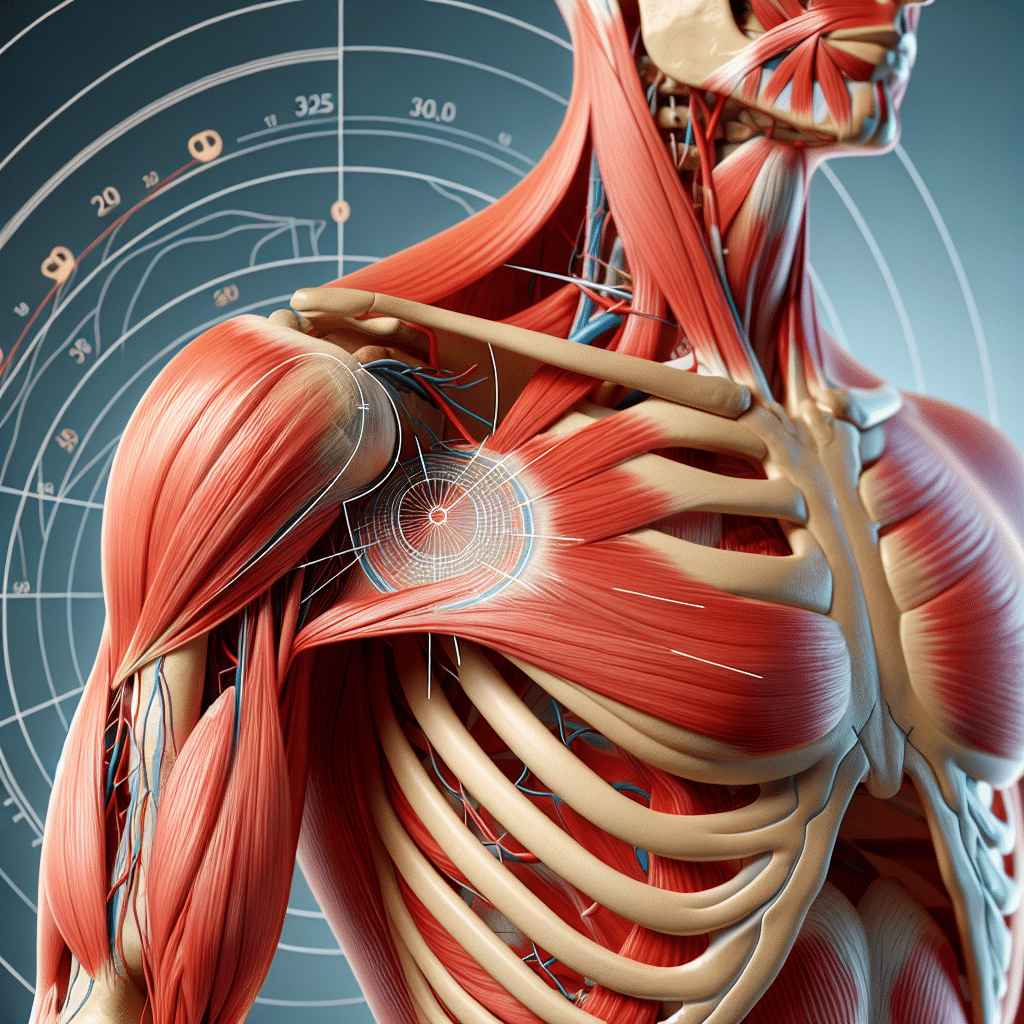
To effectively access the posterior proximal humerus, the best approaches are often through either an open surgical technique or arthroscopic methods, depending on the specific case and the surgeon’s expertise. The posterior approach typically includes a deltopectoral incision or a straight posterior incision made along the scapular spine. Utilizing a deltoid-sparing technique can minimize muscle damage and optimize recovery while the arthroscopic approach is preferred for less invasive intervention.
Surgeons will assess patient-specific factors such as fracture type, condition severity, and overall anatomy to determine the most suitable method. A thorough understanding of the surrounding neurovascular structures is critical to avoid complications. Additionally, utilizing advanced imaging techniques such as fluoroscopy or direct visualization techniques aids in ensuring precise navigation to the target area. Proper preoperative planning and familiarity with the anatomy are keys to a successful outcome.
Introduction
The posterior proximal humerus is a critical region often encountered in orthopedic procedures. Offering access to vital structures surrounding this area, understanding the best way to navigate this anatomical territory is essential for surgeons. The posterior approach provides access to the rotator cuff, glenohumeral joint, and surrounding soft tissues, making it common for repairs and assessments in cases of fractures, dislocations, or degenerative disorders.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Posterior Proximal Humerus
Before delving into access techniques, a firm grasp of the anatomy is paramount. The proximal humerus includes several key structures:
- Greater Tuberosity: The lateral prominence that serves as the attachment for rotator cuff muscles.
- Less Tuberosity: Located medially, this structure serves as the insertion point for the subscapularis muscle.
- Humeral Head: Articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula, crucial for shoulder joint mobility.
- Neurovascular Structures: The axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery are critically located in this area, necessitating careful handling during access.
Access Techniques to the Posterior Proximal Humerus
There are several surgical approaches taken when accessing the posterior proximal humerus. Each technique has its merits and can be chosen based on the specific clinical scenario.
1. Open Posterior Approach
The open posterior approach to the proximal humerus involves creating a significant incision that permits direct visualization and manipulation of the underlying structures. This approach includes:
- Incision: A straight longitudinal incision along the midline of the posterior shoulder can be utilized to expose the proximal humerus.
- Muscle Release: The deltoid and infraspinatus muscles need to be carefully retracted or incised to expose the humeral head.
This technique offers excellent visualization but may lead to muscle damage and longer recovery times.
2. Deltopectoral Approach
The deltopectoral approach is more commonly used for anterior humeral access, but it can be adapted for posterior needs:
- Incision: Starting from the deltoid insertion down toward the coracoid process allows access to the proximal aspect of the humerus while preserving deltoid muscle function.
- Visual Field Expansion: The approach allows for the retraction of the pectoralis major while giving an excellent view of the posterior aspect of the proximal humerus.
Employing this method can minimize muscle disruption and improve recovery.
3. Arthroscopic Techniques
Arthroscopy is a less invasive option that offers several advantages:
- Minimally Invasive: Small incisions are made, and a camera is inserted to guide the surgical tools.
- Less Trauma: This technique results in reduced blood loss, less pain, and faster recovery times.
However, it may not be suitable for complex fractures requiring extensive manipulation.
Choosing the Right Technique
The choice of technique primarily depends on several factors:
- Condition Severity: More severe injuries may necessitate open surgery for adequate access.
- Patient Health: The overall condition of the patient, including comorbidities, should guide the approach choice.
- Surgeon Expertise: The familiarity and proficiency the surgeon has with a particular technique can impact outcomes.
Postoperative Considerations
Regardless of the access method employed, postoperative care is crucial for successful recovery:
- Rehabilitation: A tailored rehabilitation program is vital to restore movement and strength.
- Pain Management: Effective pain control measures should be implemented to facilitate recovery.
- Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
FAQs
What are the risks associated with accessing the posterior proximal humerus?
Like any surgical procedure, accessing the posterior proximal humerus carries risks including nerve injuries (notably to the axillary nerve), vascular complications, infection, and inadequate healing.
How is the surgical approach decided?
The surgical approach is determined based on the type and severity of the injury, the specific goals of the surgery, and the surgeon’s expertise with various techniques.
Can the procedure be done arthroscopically for all cases?
Not all cases can be addressed arthroscopically; complex fractures or significant anatomical alterations may require open surgical techniques for full visualization and repair.
What is the recovery time after surgery?
Recovery time can vary widely depending on the procedure type, extending from a few weeks with arthroscopic techniques to several months for open surgery, typically involving physical therapy.
Are there any long-term effects of accessing the proximal humerus?
Long-term effects can include stiffness or weakness in the shoulder, depending on the extent of the procedure and adherence to rehabilitation programs.
Conclusion
Accessing the posterior proximal humerus involves a careful evaluation of various techniques, each suitable for different clinical scenarios. Understanding the anatomy, surgical options, and postoperative care is essential for achieving optimal patient outcomes. Ongoing advancements in surgical techniques continue to enhance accessibility and patient recovery.