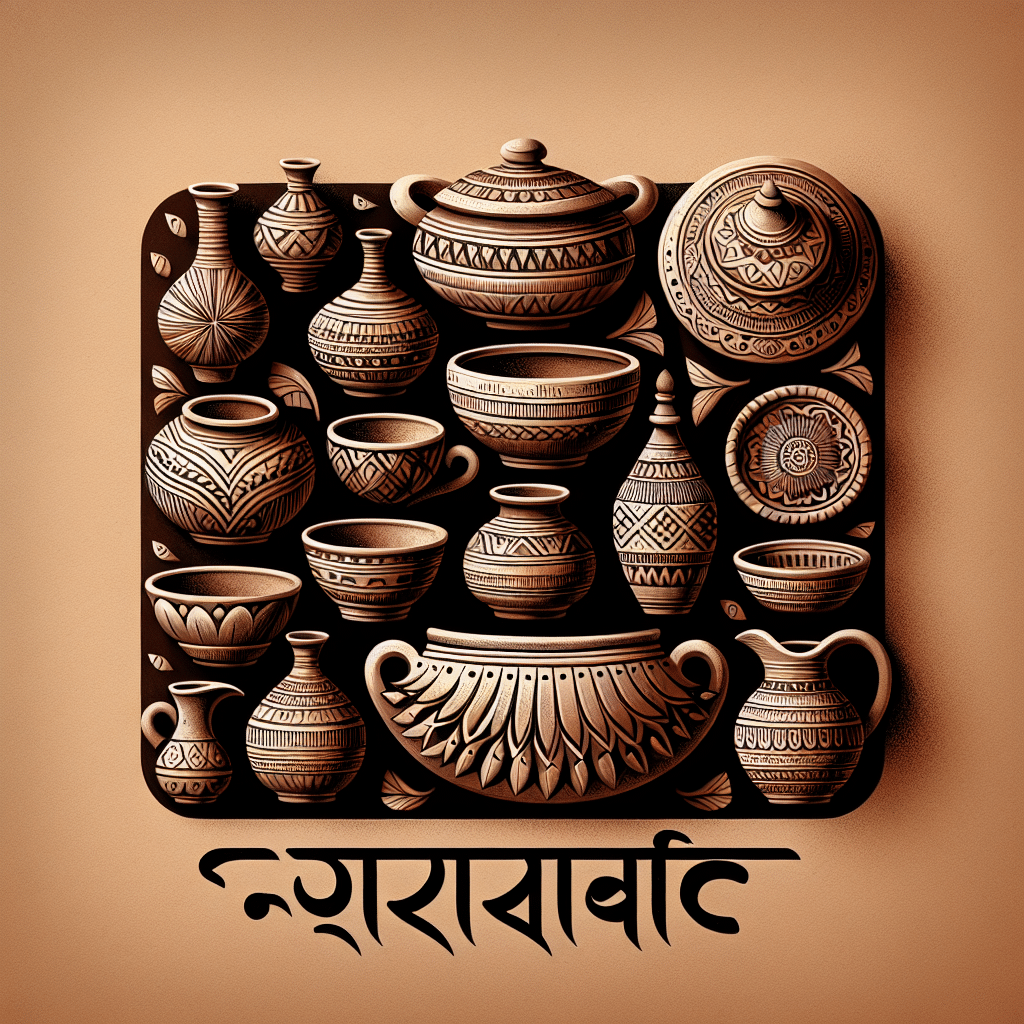
What is Earthenware in Bengali?
In Bengali, earthenware is referred to as “মাটি পাত্র” (mati patra). This term combines “মাটি” (mati), meaning soil or clay, and “পাত্র” (patra), meaning vessel or pot. Earthenware is a type of ceramics made by shaping and firing clay at low temperatures, resulting in porous, often unglazed pottery. These handcrafted items are widely celebrated in Bengali culture, known for their rich tradition of pottery that dates back centuries. Earthenware is not only functional, used for cooking or storage, but also holds cultural significance, often used in traditional ceremonies and rituals. The artistry involved in crafting earthenware reflects the local heritage, making it a vital part of Bengali craftsmanship.
Understanding Earthenware
Earthenware encompasses a broad category of pottery made from clay, with distinct characteristics that set it apart from other ceramic types such as stoneware and porcelain. When discussing earthenware, it is essential to explore its properties, manufacturing processes, and its significance in various cultures, particularly in Bengali tradition.
Composition and Characteristics
- Materials: Earthenware is primarily made from clay, which can vary depending on the region. The clay is typically rich in iron oxide, giving it a reddish color. Other additives such as sand or grog (fired and crushed clay) may be included to enhance durability and texture.
- Firing Temperature: Unlike stoneware or porcelain that requires higher firing temperatures (over 1200°C), earthenware is fired at lower temperatures (approximately 900-1100°C). This results in a porous structure that retains moisture, making it suitable for various traditional uses, including cooking.
- Finish: Traditionally, earthenware is left unglazed, which contributes to its porous nature. However, some artisans apply a glaze to enhance aesthetics and impermeability.
Manufacturing Process
- Clay Preparation: The clay is kneaded thoroughly to remove air pockets and achieve a uniform consistency.
- Shaping: Artisans use various techniques to shape the clay into desired forms, such as hand molding, wheel throwing, or slab building.
- Drying: Once shaped, the items are left to dry slowly to prevent cracking during the firing process.
- Firing: The dried items are then placed in a kiln for firing, where they undergo a physical and chemical transformation, solidifying their structure.
- Finishing: Post-firing, artisans may paint or glaze the earthenware to enhance its functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Types of Earthenware
Understanding the different types of earthenware can provide further insights into its cultural relevance and applications.
- Terracotta: This type of earthenware is known for its reddish-brown color and is often used in making pots, tiles, and sculptures. In Bengali culture, terracotta items often depict local deities or scenes from mythology.
- Stoneware: A crude ancestor of finer stoneware, this type retains a more rustic look and is used for utilitarian purposes.
- Colored Earthenware: Some artisans apply colorful glazes or paint to enhance the visual appeal, often depicting traditional motifs or geometrical patterns.
Cultural Significance in Bengali Tradition
In Bengal, earthenware holds a special place in everyday life and cultural practice. Festivals and rituals often prominently feature earthenware items:
- Puja (Worship): Earthen pots and plates are used in various religious rituals, signifying purity and natural origins.
- Harvest Tradition: During the harvest season, earthen vessels are common for storing grains and contributing to traditional ceremonies.
- Artistic Expression: Pottery in Bengal is also an art form, where artisans infuse their pieces with intricate designs, often reflecting the local flora and fauna.
Modern Applications and Sustainability
With the growing trend towards sustainable living, earthenware is regaining popularity in modern households. Its ecological advantages include:
- Biodegradable: Being made from natural clay, earthenware is biodegradable, unlike many plastic alternatives.
- Health Benefits: Cooking in earthenware is believed to enhance the flavor of food and retain essential nutrients.
- Local Economy: Supporting local artisans who craft earthenware contributes to sustainable economic practices and keeps traditional crafts alive.
FAQs About Earthenware in Bengali Culture
What Are the Common Uses of Earthenware?
Earthenware is commonly used for cooking, serving food, storing items, and in religious and cultural ceremonies, reflecting both functional and aesthetic values.
How Do I Care for Earthenware?
To care for earthenware, avoid drastic temperature changes, hand wash instead of using a dishwasher, and refrain from using metal utensils that could scratch the surface.
Is Earthenware Safe for Cooking?
Yes, earthenware is safe for cooking as long as it is intended for such use. Always check for any glazing that might not be food safe, especially in older pieces.
Why Is Earthenware Preferred in Some Cultures?
Earthenware is preferred for its natural properties, economic benefits, traditional significance, and its unique ability to enhance the flavor of food while also being aesthetically pleasing.
Conclusion
Earthenware, or “মাটি পাত্র,” is more than just clay pots; it embodies a rich tradition that is an integral part of Bengali identity. As you explore the cultural significance and practical applications of earthenware, you will gain a deeper appreciation for this ancient craft. Whether as art, utility, or a connection to heritage, earthenware continues to play a vital role in Bengali life, blending history with modern sustainable practices.