Introduction to AGM Batteries
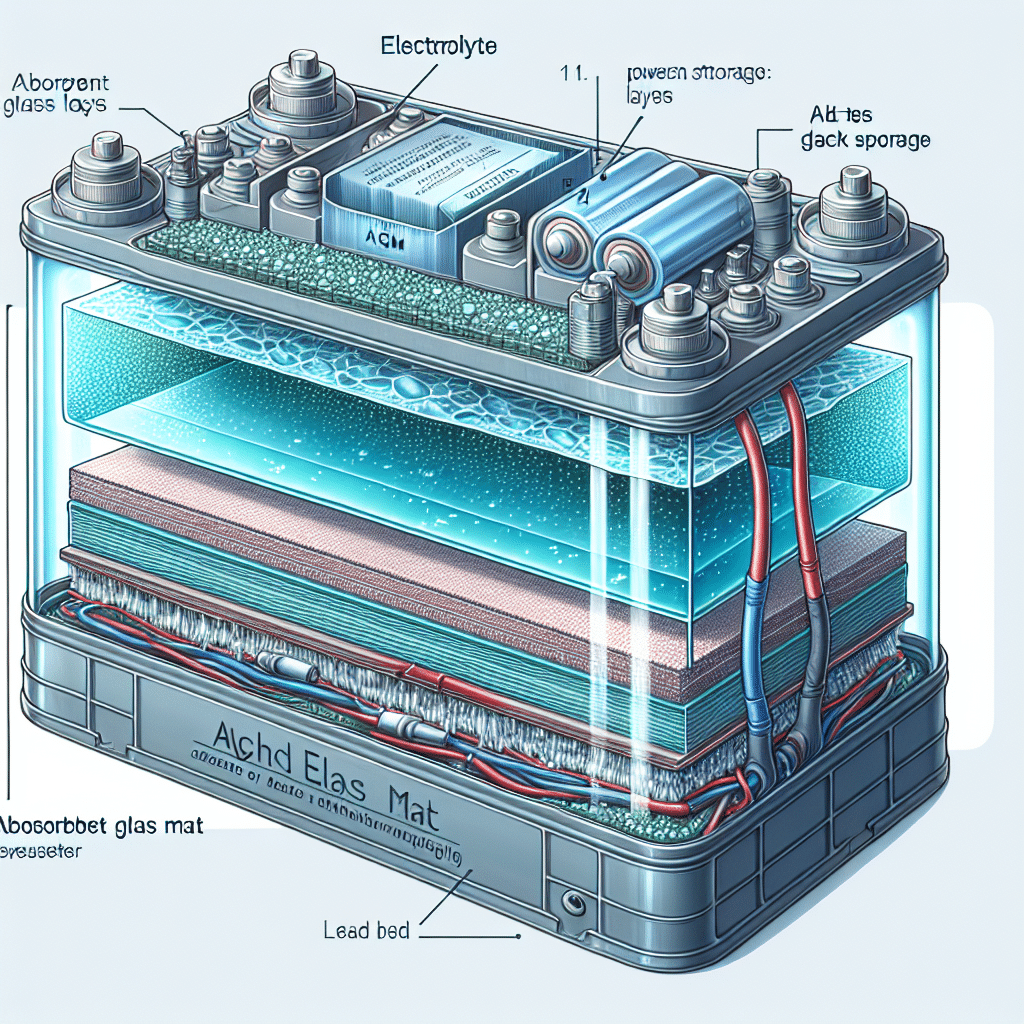
Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) batteries are a type of lead-acid battery that utilizes a unique design to enhance their performance and lifespan. These batteries feature a glass mat separator that absorbs the electrolyte, which allows for a reduced risk of spillage and permits operation in various orientations. The primary components of an AGM battery include lead plates, a sulfuric acid electrolyte, and the absorbent glass mat. This design results in several advantages, including faster recharging times, enhanced deep cycling capabilities, and lower self-discharge rates. AGM batteries are widely used in applications such as automotive, marine, and renewable energy systems, due to their durability, safety, and efficiency.
Understanding AGM Batteries: Composition and Construction
1. Components of AGM Batteries
AGM batteries consist of four main components: lead plates, an electrolyte solution, separators, and an enclosure. Each element plays a vital role in the battery’s function and performance.
-
Lead Plates:
These plates serve as the primary source of energy storage in the battery. The lead plates are composed of pure lead or lead alloy, and they serve as both the anode and cathode. The anode is the negative plate, while the cathode is the positive plate. -
Electrolyte:
The electrolyte in AGM batteries is a diluted sulfuric acid solution, which enables the flow of ions between the lead plates. The glass mat absorbs the electrolyte, preventing spillage and allowing the battery to operated in various orientations. -
Separators:
The absorbent glass mat acts as a separator between the lead plates. It holds the electrolyte and prevents short-circuiting, thus ensuring efficient energy transfer. -
Enclosure:
The outer casing is typically constructed from sturdy, durable materials, which provides protection against environmental factors and impacts while also housing the internal components securely.
2. How AGM Batteries Work
The operation of AGM batteries is based on reversible chemical reactions between the lead plates and the sulfuric acid electrolyte. During discharge, the lead and lead dioxide react with the sulfuric acid, generating lead sulfate and releasing electrical energy. When charged, the process is reversed, converting lead sulfate back into lead and lead dioxide while regenerating sulfuric acid. This process is efficient due to the unique absorbent glass mat, which facilitates faster ion movement and minimizes resistance, allowing for quicker charging and discharging cycles.
Benefits of AGM Batteries
1. Enhanced Safety
One of the main advantages of AGM batteries is their safety features. Since the electrolyte is absorbed in the glass mat, there is a decreased risk of leakage and spill, making them safe for use in any orientation. This design also makes them less prone to thermal runaway, a critical concern in traditional lead-acid batteries.
2. Longer Lifespan
AGM batteries typically have a longer cycle life compared to traditional flooded lead-acid batteries. Their ability to undergo deep cycling means that they can be discharged to a lower level without suffering from significant capacity loss, ultimately leading to a prolonged operational life.
3. Low Self-Discharge Rate
AGM batteries have an extremely low self-discharge rate, meaning they can hold their charge longer when not in use. This feature is particularly beneficial for applications where the battery may be idle for extended periods, such as seasonal vehicles or backup power systems.
4. Versatility and Application
Due to their robust construction and enhanced performance, AGM batteries are suitable for various applications, including automotive, marine, telecommunications, and renewable energy systems like solar power. They are especially valued in situations requiring deep cycling capabilities.
Disadvantages of AGM Batteries
1. Cost
AGM batteries tend to be more expensive than traditional lead-acid batteries. While their lifespan and performance may justify the cost in many applications, budget constraints may limit their use for some consumers.
2. Sensitivity to Overcharging
AGM batteries require precise charging to prevent damage. While they are less likely to leak, overcharging can lead to excessive gas buildup and shelf life reduction. Using the appropriate charger with AGM-specific settings is essential to avoid these issues.
How to Maintain AGM Batteries
1. Regular Charging
AGM batteries should be charged regularly to maintain their capacity and longevity. Using a smart charger with an appropriate charging algorithm for AGM batteries can help optimize their performance.
2. Optimal Storage Conditions
Store AGM batteries in a cool, dry environment away from extreme temperatures. This ensures that the battery remains in good condition and retains its performance levels.
3. Routine Inspections
Regularly inspect the battery for any signs of damage or corrosion. Maintaining clean terminals and ensuring a secure connection can help prevent performance issues.
AGM Battery Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the lifespan of an AGM battery?
The lifespan of an AGM battery can range from 3 to 10 years, depending on usage, maintenance, and environmental conditions. Proper care can significantly extend its life.
2. Can AGM batteries be used in cold temperatures?
Yes, AGM batteries perform well in cold conditions. However, at very low temperatures, capacity may temporarily decrease, and it’s essential to ensure they are kept adequately charged.
3. Are AGM batteries maintenance-free?
While AGM batteries require less maintenance than traditional lead-acid batteries, they are not entirely maintenance-free. Regular charging and inspection are still needed.
4. Can you use a regular charger for AGM batteries?
It is best to use a charger designed for AGM batteries. Regular chargers may overcharge or undercharge the battery, leading to reduced performance and lifespan.
5. Are AGM batteries suitable for solar systems?
Yes, AGM batteries are commonly used in solar energy systems because of their deep cycling capabilities and low self-discharge rates, making them an excellent choice for energy storage.
Conclusion
Understanding what constitutes an AGM battery is crucial for users looking to optimize their energy storage solutions. By offering a blend of safety, durability, and efficiency, AGM batteries cater to various applications across different industries. However, it is essential to recognize their limitations and follow best practices for maintenance to ensure maximum performance and longevity. As you explore options for power solutions, considering AGM batteries could be a beneficial choice tailored to your specific needs.