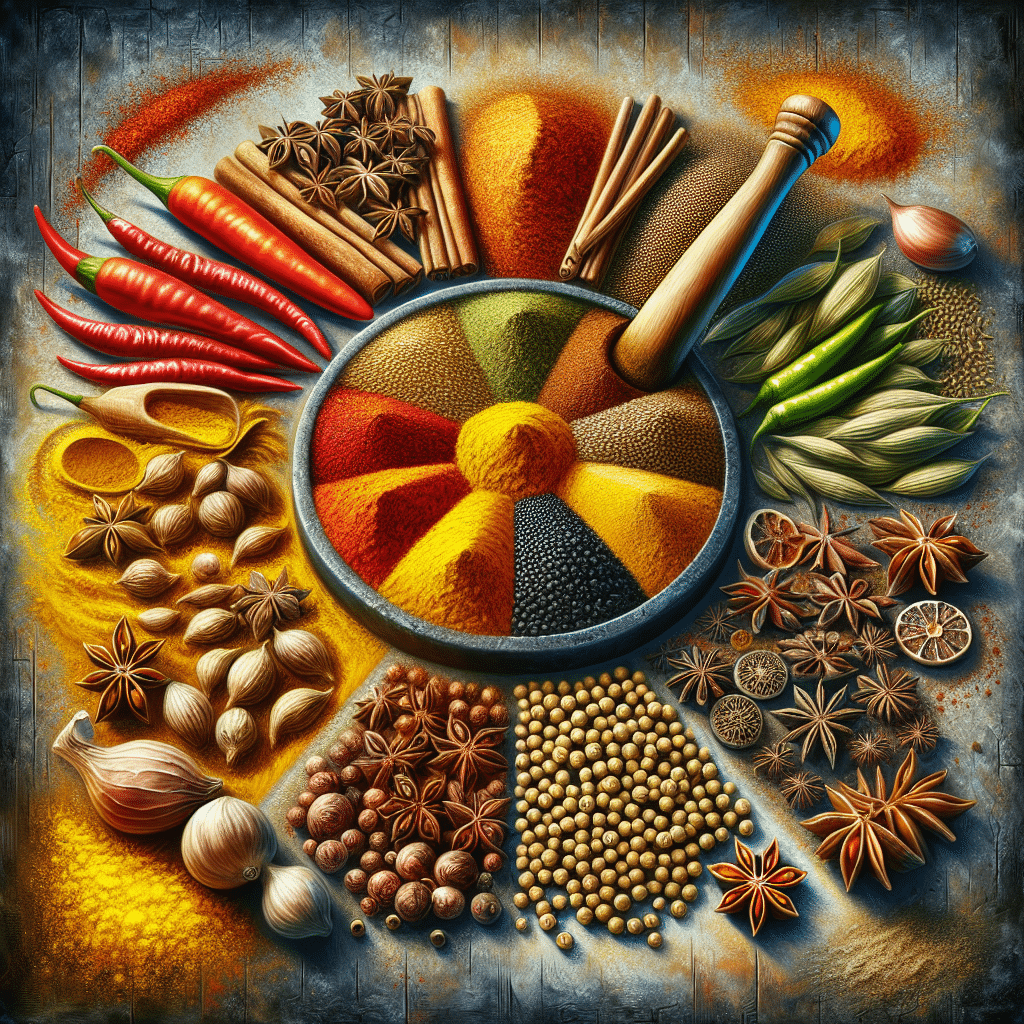
What is in curry powder? Curry powder is a spice blend used primarily in South Asian cuisine, known for its distinct flavor and vibrant color. The primary components typically include turmeric, coriander, cumin, and fenugreek, along with various other spices such as ginger, cinnamon, and black pepper. Turmeric is particularly notable for providing curry powder with its characteristic yellow hue, associated with numerous health benefits, including anti-inflammatory properties. While there are regional variations, most curry powders are crafted to achieve a balance between warmth, brightness, and earthiness, enhancing the flavor profile of various dishes. The exact composition can vary among different brands and personal recipes, allowing for a wide range of aromatic preferences and culinary applications.
Understanding Curry Powder: A Flavorful Spice Blend
Curry powder is more than just a single spice; it’s a rich and complex blend that varies significantly depending on the region, cuisine, and cultural traditions involved. Originating from the Indian subcontinent, this spice mixture has transcended its geographical boundaries, becoming a staple in kitchens worldwide, particularly in the United States.
Ingredients of Curry Powder
The specific ingredients in curry powder can differ widely, but several key spices are almost universally present:
- Turmeric: This bright yellow spice is essential in curry powder. It not only imparts a vivid color but also possesses several health benefits, such as anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Coriander: Ground coriander seeds add a mild, citrusy flavor that complements the warmth of other spices.
- Cumin: This spice brings a deep, earthy flavor profile, enhancing the overall complexity of the blend.
- Fenugreek: Fenugreek seeds contribute a slightly sweet, nutty taste and have been used traditionally in Ayurvedic medicine.
- Ginger: Ground ginger adds a hint of warmth and spice, balancing the other flavors within the blend.
- Cinnamon: Used in some variations, cinnamon provides a sweet note that contrasts with the more pungent spices.
- Black Pepper: Freshly ground black pepper can enhance the pungency and introduce a subtle heat.
Other optional ingredients may include garlic powder, chili powder, cloves, cardamom, and mustard powder, all of which serve to create unique flavor profiles. The combination of these spices is intended to produce balance, where no one spice overpowers the others, making curry powder extremely versatile for various dishes beyond traditional curries, including soups, marinades, and even seasoning for roasted vegetables.
The Regional Variations of Curry Powder
While the ingredient list above outlines a typical curry powder, the nuances of regional variations bring additional depth. For example:
- Indian Curry Powder: Often contains dried curry leaves and is more peppery, with an emphasis on pungency and heat.
- Thai Curry Powder: Incorporates lemongrass and galangal, giving it a fragrant and distinctive character, suitable for green and red curries.
- Japanese Curry Powder: Typically milder and sweeter compared to its Indian counterpart; it may include apples or honey in the blend.
Health Benefits of Curry Powder
Curry powder is not just a flavorful addition to meals; it also packs a punch when it comes to health benefits. Some notable advantages include:
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Curcumin, the active ingredient in turmeric, has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory effects, potentially helping to manage conditions like arthritis.
- Antioxidant Effects: The antioxidants in curry powder can combat oxidative stress, reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Digestive Health: Many spices found in curry powder, such as ginger and coriander, can aid digestion and promote gut health.
How to Use Curry Powder in Cooking
Incorporating curry powder into your cooking is simple and can elevate a variety of meals:
- Curries: The most obvious use is in curry dishes, where the blend serves as a base flavor.
- Soups and Stews: Add curry powder to soups for an aromatic twist, such as in coconut milk-based soups or lentil stews.
- Marinades: Mix with yogurt or oil to create marinades for meats and vegetables, infusing them with flavor.
- Roasted Vegetables: Sprinkle curry powder on vegetables before roasting for a warm, spiced finish.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between curry powder and garam masala?
Curry powder is typically used for preparing dishes before cooking, while garam masala is a finishing spice blend added for flavor enhancement just before serving. They have different spice compositions and flavor profiles; curry powder often emphasizes earthy notes, while garam masala tends to be warmer and sweeter.
2. Is curry powder gluten-free?
Most curry powders are gluten-free, but it’s advisable to check the label or specifics of the brand, as cross-contamination can occur during manufacturing.
3. Can I make my own curry powder at home?
Absolutely! Creating your own blend allows you to customize the flavors. A simple recipe would include equal parts of turmeric, coriander, cumin, and optional spices like fenugreek or black pepper, to taste.
4. How should curry powder be stored?
To maintain freshness, store curry powder in a cool, dark place, preferably in an airtight container to prevent moisture and oxidation. Proper storage can extend its shelf life for up to two years.
5. Can curry powder be used in non-curry recipes?
Yes! Curry powder can spice up a wide range of dishes, including grain salads, scrambled eggs, roasted meats, and even salad dressings, introducing unique flavors beyond traditional usage.
Conclusion
Curry powder stands out as a versatile and flavorful spice blend that can be utilized in various culinary practices. By understanding its core ingredients, health benefits, and applications in cooking, you can enhance your culinary experiences while also enjoying the health advantages that come with this vibrant spice. Experimenting with different regional blends may also provide an exciting exploration of flavors that expands your palate and enriches your cooking repertoire.