Introduction
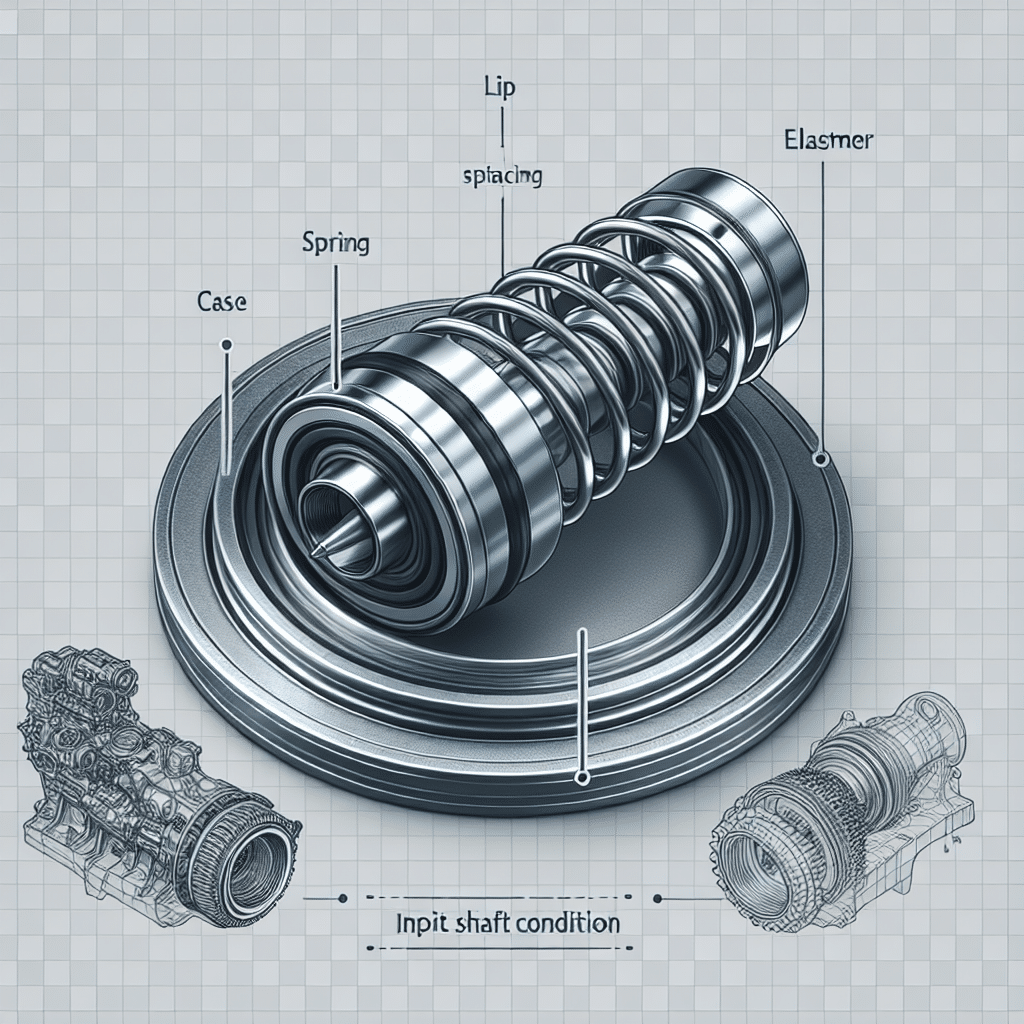
An input shaft seal is a vital component in automotive and machinery systems, serving as a barrier to prevent fluids from leaking in and out of the gearbox or transmission. These seals are designed to protect the internal components from dirt, debris, and fluids, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. When functioning correctly, an input shaft seal maintains the integrity of the system, enhances performance, and reduces wear. Should a seal fail, it can lead to serious issues, including fluid leaks and damage to the transmission or differential systems. Understanding the importance and function of the input shaft seal can help vehicle owners and technicians ensure a reliable and smooth operation.
What is an Input Shaft Seal?
The input shaft seal is a type of oil seal installed around the input shaft, which is the component that transmits engine power to the drivetrain or transmission. This seal is crucial for maintaining the system’s hydraulic integrity, as it helps to prevent any leakage of lubricants, such as oil or transmission fluid, while also keeping contaminants out of the internal workings of the system.
Function and Importance of Input Shaft Seals
Input shaft seals serve multiple functions within a vehicle’s drivetrain:
- Fluid Retention: They help to keep the lubricant contained within the gearbox, ensuring proper lubrication of moving parts.
- Contaminant Protection: By preventing dirt and debris from entering the transmission, seals protect sensitive components from wear and damage.
- Pressure Maintenance: Seals maintain the correct pressure within the system, crucial for optimal performance.
Common Materials Used
Input shaft seals are typically made from a variety of materials that are chosen for their resilience and compatibility with the fluids they will encounter. Some of the common materials include:
- Rubber: Most common, providing excellent flexibility and sealability.
- PTFE (Teflon): Known for its chemical resistance and low friction properties.
- Polyurethane: Offers durability and wear resistance, commonly found in high-performance applications.
Installation of Input Shaft Seals
Proper installation of input shaft seals is critical for their efficient operation. Here’s a general overview of the installation process:
- Remove the Old Seal: Using the appropriate tools, carefully extract the old input shaft seal.
- Clean the Area: Ensure that the seal housing and shaft are clean to avoid any debris that could compromise the new seal’s effectiveness.
- Install the New Seal: Apply a small amount of lubricant to the outer edge of the new seal and gently press it into place, ensuring it is seated evenly.
- Reassemble Components: Once the seal is installed, reassemble any components removed during the process.
Signs of a Failing Input Shaft Seal
Recognizing the early signs of a failing input shaft seal can save costly repairs down the line. Common indicators include:
- Fluid Leaks: Visible leaks around the area where the input shaft meets the transmission.
- Transmission Fluid Level Drops: Frequent need to add fluid can indicate a failing seal.
- Noisy Operation: Unusual noises from the transmission may suggest problems related to lubrication.
Maintenance Tips
To enhance the lifespan of input shaft seals, consider the following maintenance tips:
- Regular Fluid Checks: Regularly inspect fluid levels and quality. Low or dirty fluid can lead to premature seal failure.
- Timely Inspections: During routine maintenance, inspect seals for signs of wear or damage.
- Proper Parts Usage: Use OEM or high-quality replacement parts during repairs to ensure compatibility and longevity.
Common Myths About Input Shaft Seals
Several misconceptions exist regarding input shaft seals:
- Myth 1: “I can ignore fluid leaks.”
Truth: Ignoring leaks can lead to serious damage and expensive repairs. - Myth 2: “Seals last the lifetime of the vehicle.”
Truth: Like many components, seals have a lifespan and may require replacement. - Myth 3: “All seals are the same.”
Truth: Using the wrong type or size can lead to failure and leaks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the average lifespan of an input shaft seal?
The lifespan of an input shaft seal can vary depending on the usage and conditions but typically ranges from 50,000 to 100,000 miles. Regular maintenance can significantly extend its life.
Can I replace an input shaft seal myself?
With the right tools and precautions, replacing an input shaft seal can be a DIY project. However, if you are unfamiliar with automotive repairs, seeking professional assistance is recommended.
What could happen if I ignore a bad input shaft seal?
Ignoring a failing seal can lead to fluid leaks, overheating of the transmission, and ultimately severe transmission damage, which can be costly to repair.
How much does it cost to replace an input shaft seal?
Replacement costs can vary widely but typically range from $150 to $500, depending on labor costs, location, and the specific vehicle model.
Conclusion
The input shaft seal is a crucial component responsible for ensuring the operational integrity of a vehicle’s drivetrain. Understanding its function, signs of failure, and proper maintenance techniques can prevent costly repairs and extend the longevity of your vehicle. If you suspect an issue with your input shaft seal, it’s best to consult a qualified technician to address it promptly.