Introduction to Manufactured Wood
Manufactured wood, also known as engineered wood, refers to a range of wood-based products made by binding or fixing the strands, particles, fibers, or veneers of wood together with adhesives or mechanical means. Unlike solid wood, manufactured wood is designed for better durability and versatility, addressing some of the shortcomings of traditional lumber. Common types of manufactured wood include plywood, oriented strand board (OSB), medium-density fiberboard (MDF), and particle board. These products are widely used in construction, furniture making, and cabinetry due to their cost-effectiveness, strength, and ease of use. Understanding the characteristics, advantages, and applications of manufactured wood is crucial for making informed decisions in various projects.
What is Manufactured Wood?
Manufactured wood encompasses a variety of wood products created using innovative techniques that enhance the natural properties of wood. This category of materials includes engineered products like plywood, composite wood, and fiberboard, in which raw wood undergoes transformation through methods that enhance its functionality and appearance. The definition broadens the understanding of wood as merely solid timber, illustrating its adaptability for modern applications.
Types of Manufactured Wood
Plywood
Plywood consists of thin layers of wood veneer glued together in alternating grain directions to enhance strength and stability. Available in various grades and thicknesses, plywood is widely used in structural applications ranging from flooring to wall sheathing.
Oriented Strand Board (OSB)
OSB is made from strands of wood that are oriented at right angles to each other and bonded with resin. It’s known for its excellent load-bearing capabilities and moisture resistance, making it a preferred choice in both residential and commercial construction.
Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF)
MDF is produced by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into wood fibers, combining them with wax and resin, and then forming panels under heat and pressure. Its smooth surface makes it ideal for paint finishes, making it popular for cabinetry and molded designs.
Particle Board
Particle board is created by compressing wood chips, sawmill shavings, or even sawdust. It’s an economical choice for furniture and cabinetry but generally less durable than MDF or plywood.
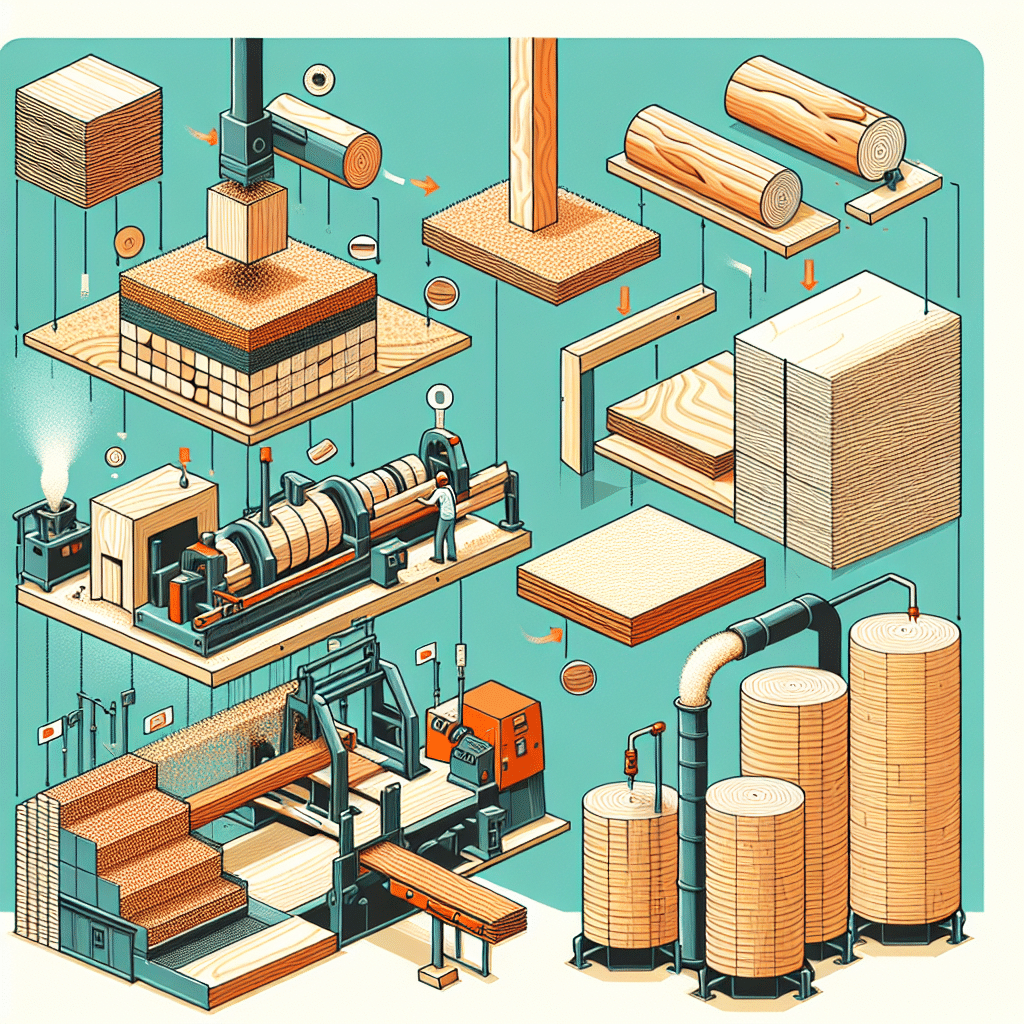
Process of Creating Manufactured Wood
The production of manufactured wood typically involves several key steps:
- Raw Material Selection: The process begins with selecting high-quality wood residues or logs.
- Processing: The wood is broken down into smaller components such as strands, flakes, or fibers.
- Bonding: Adhesives are applied to bind the components, which are then pressed into sheets or boards.
- Finishing: The products are sanded and cut to specified dimensions, ready for distribution or use.
Benefits of Manufactured Wood
Manufactured wood offers numerous benefits, making it a favored option in several applications:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Manufactured wood products are often less expensive than solid wood, making them accessible for various budgets.
- Consistency: Engineered wood provides consistency in size and quality, minimizing defects associated with natural wood.
- Environmental Impact: Utilizing wood waste and by-products reduces the demand for harvested timber, promoting sustainability.
- Versatility: Manufactured wood can be molded and shaped easily, making it suitable for diverse applications from furniture to building materials.
Applications of Manufactured Wood
Manufactured wood is widely used across several industries due to its advantageous properties:
- Construction: Plywood and OSB are typically used in framing, flooring, and roofing applications.
- Furniture Making: MDF and particle board are common materials for creating cabinets, tables, and bookshelves.
- Interior Design: Engineered wood is favored for decorative finishes, paneling, and moldings where aesthetic appearance is essential.
Durability and Maintenance
While manufactured wood is generally durable, it’s important to note that its maintenance varies depending on the type and application. Products like plywood and OSB are typically resistant to warping, whereas fiberboard may require careful handling to avoid damage from moisture. For optimal longevity, consider using seals and finishes that protect against wear and tear.
Counterarguments: Concerns and Considerations
Despite the many advantages of manufactured wood, there are valid concerns that warrant attention:
- Off-Gassing: Some engineered wood products may release formaldehyde or other volatile organic compounds, leading to health concerns in indoor environments.
- Durability in Extreme Conditions: While engineered wood is resistant to many stressors, it can still be vulnerable in extreme weather conditions compared to solid wood.
It is essential to choose products that meet regulatory standards and certifications, such as those set by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the Composite Panel Association (CPA).
Conclusion
Manufactured wood represents a crucial innovation in the material science of woodworking. By understanding the various types, benefits, and applications of engineered wood products, you can make informed decisions that align with your specific needs—whether it be for construction, furniture creation, or design projects. With considerations for sustainability and functionality, manufactured wood is set to continue its influential role in various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between manufactured wood and solid wood?
Manufactured wood refers to products made from wood fibers or veneers bonded together, while solid wood is comprised of solid timber from trees. Manufactured wood often offers better consistency and cost-effectiveness, but solid wood is prized for its durability and natural aesthetic.
Is manufactured wood environmentally friendly?
Manufactured wood can be environmentally friendly as it often utilizes wood waste and is produced in a manner that minimizes resource waste. However, it is important to check certifications and sourcing practices to ensure sustainability in production.
Can manufactured wood be used outdoors?
Some types of manufactured wood, like marine-grade plywood, are engineered for outdoor use, while others may not withstand moisture well. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications regarding suitability for outdoor applications.
How do I maintain manufactured wood products?
Maintenance of manufactured wood products typically involves cleaning with mild soaps, avoiding excess moisture, and applying appropriate finishes to protect against wear. Each product type may have specific care requirements.