What is the abbreviation of i.d and o.d electric?
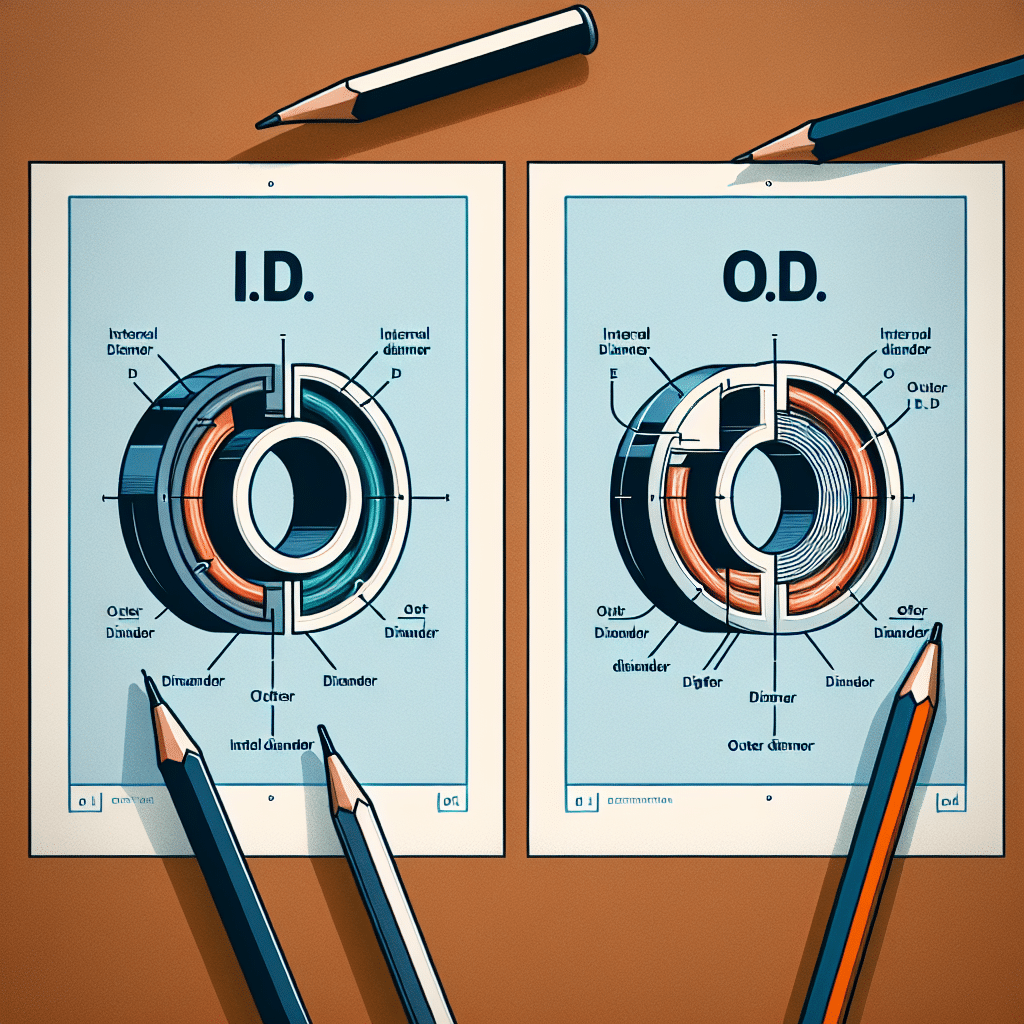
The abbreviations i.d. and o.d. are commonly used in the context of electric systems, particularly when dealing with conduits, cables, and pipes. Here, i.d. stands for “inner diameter,” which refers to the measurement of the inside space of a conduit or piping system, allowing for the accommodation of wires or fluids within it. In contrast, o.d. stands for “outer diameter,” which indicates the total width from one edge of the material to the opposite edge, encompassing the thickness of the material itself. Understanding these measurements is crucial for ensuring proper fit and functioning of electrical components, and for adhering to engineering standards. By accurately measuring i.d. and o.d., professionals can ensure compatibility and optimal performance in electric systems.
Understanding i.d. and o.d. in Electric Systems
When working with electric systems, it is imperative to have a clear grasp of key terminologies, particularly the concepts of inner diameter (i.d.) and outer diameter (o.d.). Both terms play a vital role in determining the specifications and applicability of various electrical components, including cables, conduits, and related equipment. This understanding ensures proper installation, reliability, and safety within electrical systems.
What is Inner Diameter (i.d.)?
The inner diameter, abbreviated as i.d., is an essential measurement that defines the diameter of the internal space of a cylindrical object such as a pipe or conduit. This dimension is critical for several reasons:
- Conduit Size Determination: When selecting conduits for electrical installations, knowing the i.d. is vital. It determines the amount of wiring or cables that can safely pass through without risking overheating or electrical failure.
- Fluid Flow Measurement: In applications where liquids or gases are channeled through piping, the i.d. affects flow rates and pressure. An inadequate i.d. can lead to blockages or inefficient fluid dynamics.
- Compatibility with Electrical Components: Ensuring that electrical cables fit within a conduit without excessive tension is imperative. Accurate i.d. measurements help in preventing damage to cables.
What is Outer Diameter (o.d.)?
Outer diameter (o.d.) is the measurement that encompasses the entire width of a cylindrical object. This includes the thickness of the material itself. Understanding o.d. is crucial for several reasons:
- Material Selection: The o.d. influences the choice of materials when constructing conduits or cables. A thicker o.d. may provide enhanced protection against mechanical damage.
- Installation Compatibility: Knowing the o.d. is essential for ensuring the compatibility of fittings and brackets in electrical installations. This ensures that devices hold firmly without introducing strain or misalignment that could harm the electrical integrity.
- Physical Space Requirements: In installations where spatial constraints are present, o.d. measurements assist in determining whether a specific installation will fit within dedicated areas.
Why Are These Measurements Important?
Understanding the significance of both i.d. and o.d. when working with electric systems is crucial for several reasons:
- Safety: Incorrect installations, whether involving compromised clearances or incompatible components, can lead to dangerous electrical failures.
- Efficiency: Ensuring proper fitting aids in maintaining optimal electrical performance and longevity of components.
- Compliance with Standards: Adhering to industry standards and codes relies heavily on accurate i.d. and o.d. measurements, which promotes safety and reliability within electrical systems.
Practical Examples of i.d. and o.d. in Electrical Applications
To provide a clearer understanding, let’s look at practical examples where these measurements play a critical role:
- Electrical Conduits: For instance, if an electrician is installing conduit to protect wiring runs, they must ensure the i.d. is adequate to accommodate the number and gauge of wires, while the o.d. should fit securely into mounting brackets.
- Automotive Wiring: In automotive applications, the i.d. and o.d. of wiring harnesses can determine compatibility with connectors and junction points in both electric and hybrid vehicles, where space is at a premium.
- HVAC Systems: In HVAC systems that utilize ducts, the o.d. of the ductwork needs to harmonize with flanges and other junctions, while the i.d. impacts airflow rates and efficiency.
Measurement Standards and Tools
Accurate measurement of i.d. and o.d. typically employs a variety of tools, including:
- Calipers: A digital or manual caliper is ideal for measuring small to moderate-sized pipes accurately. They can measure both internal and external dimensions smoothly.
- Gauges: Specialized gauges help ensure the right fit for specific applications, particularly in tight areas.
- Micrometers: For more precision, micrometers are employed to measure thickness, which affects both i.d. and o.d.
Common Questions About i.d. and o.d. in Electric Systems
What is the difference between i.d. and o.d.?
The primary difference between i.d. and o.d. is that i.d. refers to the inner measurement of a cylindrical object, whereas o.d. represents the outer measurement. i.d. concerns the usable internal space, while o.d. encompasses the entire external surface.
How do i.d. and o.d. influence electrical safety?
Correctly measuring i.d. and o.d. is crucial to ensure that electric cables fit properly within conduits, preventing damage due to excessive tension or overheating, and maintaining safety standards in installations.
What tools are recommended for measuring i.d. and o.d.?
Digital or manual calipers, gauges, and micrometers are commonly used tools that provide accurate measurements for both i.d. and o.d. in various applications.
Can i.d. and o.d. affect the performance of electrical systems?
Absolutely. Both measurements influence how well electrical systems operate, impacting factors like capacity for wiring, efficiency, and overall safety during operation.
In conclusion, understanding the abbreviations i.d. and o.d. is crucial for anyone working within the electrical domain. By grasping the significance of these measurements, professionals can ensure compatibility and safety in all electrical installations, leading to improved performance and reliability. As you engage with electrical components, always prioritize accurate measurements to uphold industry standards and promote safe operations.