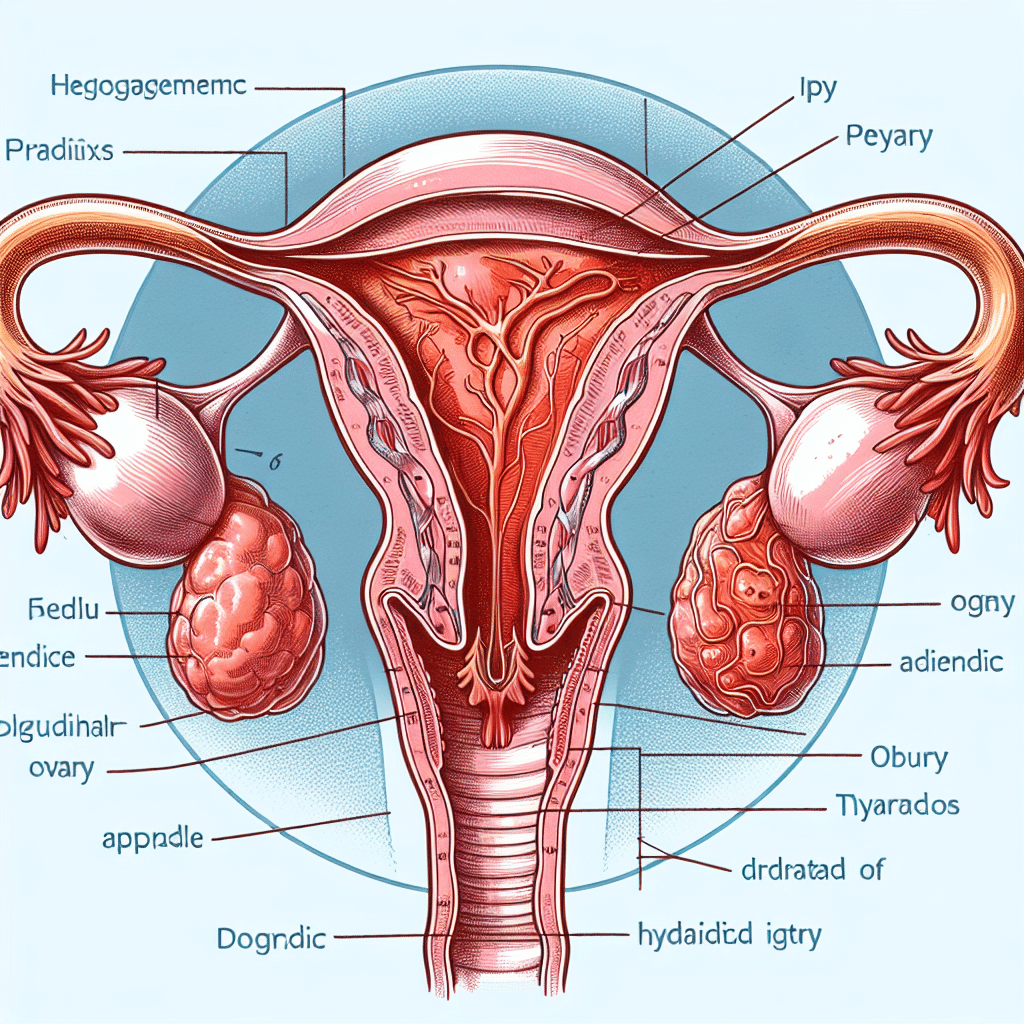
The appendix of the ovary, also known as the “paraoophoron,” is a small anatomical structure found in female reproductive anatomy. It is situated near the ovary and is part of the developmental remnants of the embryonic mesonephros, which plays a significant role in female reproductive development. This structure is typically not actively involved in reproductive function but can have clinical significance, particularly concerning conditions like ovarian torsion, cysts, or tumors. Understanding the appendix of the ovary is vital for healthcare professionals, as it can help in diagnosing potential reproductive health issues.
Overview of the Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system consists of several key components that work together to facilitate reproduction, including the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina. Each part has specific roles, from hormone production to fertilization and gestation. The ovaries, which contain follicles that develop into eggs, are particularly critical, and the appendix of the ovary, while often overlooked, contributes to the anatomical understanding of this complex system.
What is the Appendix of the Ovary?
The appendix of the ovary is a remnant of the mesonephric duct and is typically present as a small tubular structure associated with the ovary. In most females, it is a vestigial organ, meaning it is a remnant of a structure that had a functional role during earlier stages of development but has since lost its primary purpose. Although it is relatively small in size, its presence is noteworthy, especially in the context of embryology and reproductive anatomy.
Embryological Development
During embryonic development, the appendix of the ovary originates from the mesonephric ducts, also known as Wolffian ducts. In females, these ducts typically regress, but remnants may persist in the form of structures like the appendix of the ovary and the paraoophoron. This development is crucial for understanding abnormalities that may arise during maturation.
Role of the Appendix of the Ovary
While the appendix of the ovary does not play a direct role in ovarian function or reproduction, it may still have some indirect contributions to reproductive health. Its anatomical relationship to the ovary means that it can sometimes be involved in various gynecological pathologies, including:
- Ovarian Cysts: These fluid-filled sacs can develop near the ovary, sometimes affecting or involving the appendix.
- Ovarian Torsion: In cases where the ovaries twist, the anatomical position of the appendix may complicate clinical presentations.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Infections in the pelvic area can affect surrounding structures, including the appendix of the ovary.
Clinical Significance
The clinical importance of the appendix of the ovary often arises in diagnostic imaging or surgical settings. Understanding its typical anatomical location helps healthcare providers differentiate between healthy ovarian structures and pathological conditions. For example, imaging studies (like ultrasound) must accurately assess the appendix of the ovary to provide a clear diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Associated Abnormalities
While the appendix of the ovary is generally asymptomatic, there are situations where abnormalities may arise, including:
1. Paraoophoritis
Inflammation of the paraoophoron can occur due to infection or other inflammatory conditions, often presenting with pelvic pain or discomfort.
2. Cysts and Tumors
Though rare, neoplastic growths may develop in or around the appendix of the ovary. Proper imaging and clinical evaluation are necessary for distinguishing these from more common ovarian cysts.
3. Anatomical Variations
Some individuals may exhibit anatomical variations in the appendix of the ovary, which could influence certain surgical procedures or approaches to gynecological treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing issues related to the appendix of the ovary typically involves a combination of patient history, clinical examination, imaging techniques, and sometimes even exploratory surgery. Key methods include:
- Ultrasound: This is the first line of evaluation, providing images of the ovaries and surrounding structures.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI can be more detailed in assessing the state of the reproductive organs.
- Laparoscopy: In certain cases, a minimally invasive surgical procedure may be necessary for definitive diagnosis and treatment.
Management of discovered abnormalities often requires a multidisciplinary approach, where gynecologists, radiologists, and potentially oncologists collaborate to determine the best course of action, whether surgical or non-surgical.
Precautionary Measures
Regular gynecological check-ups can facilitate early detection of potential issues related to the appendix of the ovary or surrounding structures. Women are advised to report any unusual symptoms, such as pelvic pain, irregular menstrual cycles, or abnormal bleeding, to ensure timely evaluation and intervention if necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the function of the appendix of the ovary?
The appendix of the ovary is primarily a vestigial structure without any known significant function in present human anatomy. However, it may involve incidental findings during medical examinations.
Can the appendix of the ovary become inflamed?
While less common, inflammation can occur in or around the appendix of the ovary, often due to pelvic inflammatory disease or other infections, presenting with symptoms similar to other gynecological problems.
Is surgery necessary for issues related to the appendix of the ovary?
Not all conditions involving the appendix of the ovary require surgery. However, if abnormalities like cysts or torsion are detected and deemed symptomatic or problematic, surgical intervention may be necessary to alleviate pain and prevent further complications.
How can I maintain ovarian health?
Maintaining ovarian health involves regular health check-ups, a balanced diet, exercise, and monitoring any changes in menstrual cycles or symptoms. Promptly addressing any gynecological concerns with a healthcare professional is also crucial.
Conclusion
While the appendix of the ovary may not have a prominent role in female reproductive health, its existence and possible implications are significant within the broader context of gynecological anatomy and disease. Understanding its structure and potential effects can assist healthcare professionals in their practice and provide insights into female reproductive health. As knowledge about this anatomical feature deepens, it underscores the importance of holistic approaches to women’s health.