Introduction
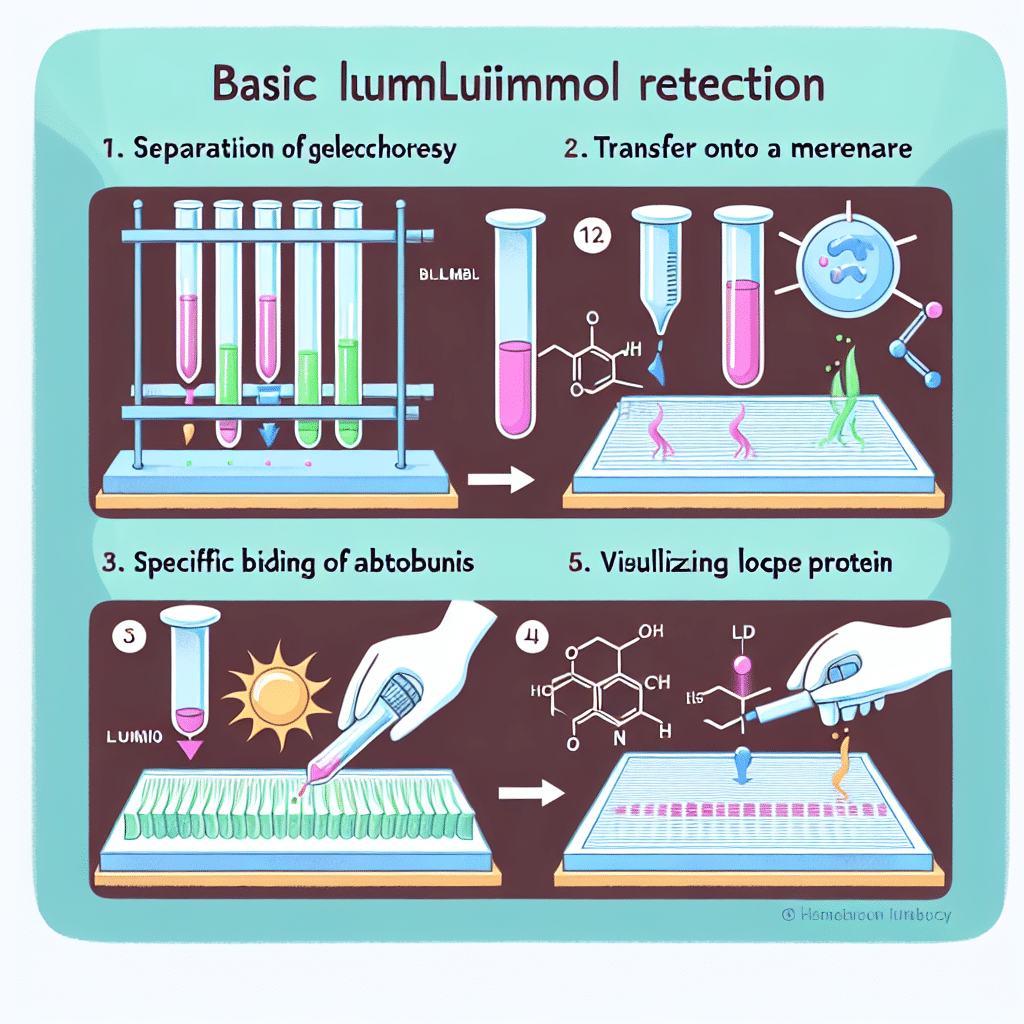
The basic lumimol reaction for Western blot detection is a critical component in visualizing proteins within a sample. This reaction involves the use of luminescent substrates, specifically luminal, which, in the presence of an enzyme such as horseradish peroxidase (HRP), produces a light signal corresponding to the amount of target protein in the sample. This chemiluminescence allows for sensitive and quantitative detection, making it a preferred method in numerous research applications. The lumimol reaction is initiated when the substrate is catalyzed by HRP in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, resulting in the emission of light that can be captured on imaging systems, highlighting specific protein bands on the blot. By providing high sensitivity and the ability to detect low abundant proteins, the basic lumimol reaction is indispensable for reliable protein analysis in biomedical research.
Understanding the Lumimol Reaction
The lumimol reaction is at the heart of chemiluminescent detection methods used in Western blotting. When proteins are separated by gel electrophoresis and transferred onto a membrane, the specific proteins of interest can be detected using antibodies. The use of luminescent substrates provides a highly sensitive means of visualizing these proteins.
Mechanism of the Lumimol Reaction
In essence, the basic lumimol reaction requires the following key components:
- Luminal: This is the luminescent substrate that generates light upon reaction.
- Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP): An enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of luminal in the presence of hydrogen peroxide.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: This serves as an oxidizing agent in the reaction.
The reaction proceeds as follows:
- When luminal is combined with hydrogen peroxide and HRP, the enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of luminal to produce an electronically excited state.
- This excited state then relaxes to a lower energy state, emitting light in the process.
- The intensity of the emitted light is directly proportional to the amount of target protein bound to the antibody conjugated with HRP on the blot.
Applications in Western Blotting
The lumimol reaction’s sensitivity makes it particularly valuable in various applications:
- Detection of Low Abundance Proteins: Researchers can accurately detect and quantify proteins that are present in very low levels.
- Gene Expression Studies: It enables the analysis of protein expression levels in different biological samples.
- Clinical Diagnostics: Allows for the detection of disease markers in blood samples, enhancing diagnostic precision.
Advantages of Using Lumimol Reaction
The advantages of employing the lumimol reaction in Western blotting include:
- High Sensitivity: Capable of detecting picogram amounts of proteins.
- Wide Dynamic Range: Useful for quantifying a broad range of protein concentrations.
- Rapid Results: Allows for a quick assessment of protein presence and quantity.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite its numerous advantages, there are some limitations to consider when using the lumimol reaction:
- Limited Shelf Life: Luminescent substrates may degrade over time, affecting efficacy.
- Non-Reusability: Once the reaction occurs, the light emitted cannot be reused for additional analysis.
- Background Noise: Potential for non-specific binding that can lead to background signal.
FAQs on Lumimol Reaction in Western Blotting
What is the role of horseradish peroxidase in the lumimol reaction?
HRP catalyzes the oxidation of luminal in the lumimol reaction, facilitating the conversion of substrate to light-emitting products. Its activity is crucial for generating a detectable signal.
Can lumimol reaction be used for other types of detection aside from Western blotting?
Yes, the lumimol reaction is versatile and can be applied in various immunoassays and detection systems, including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and in situ hybridization.
How can I enhance the specificity of the lumimol reaction?
Enhancing specificity can be achieved by optimizing antibody concentration, using specific blocking agents, and ensuring proper washing to reduce nonspecific binding.
Are there alternative substrates to luminal for chemiluminescent detection?
Yes, there are several alternatives such as Enhanced Chemiluminescence (ECL) substrates, which offer improved signal-to-noise ratios and longer signal duration.
Conclusion
The basic lumimol reaction represents an essential technique in Western blot detection, providing scientists with a sensitive and effective means of quantifying proteins in biological samples. While it offers significant advantages in terms of sensitivity and specificity, understanding the limitations and careful optimization can enhance its effectiveness in research applications. As protein analysis continues to play a pivotal role in biomedical sciences, the lumimol reaction remains a cornerstone in the methodology of Western blotting.