Introduction
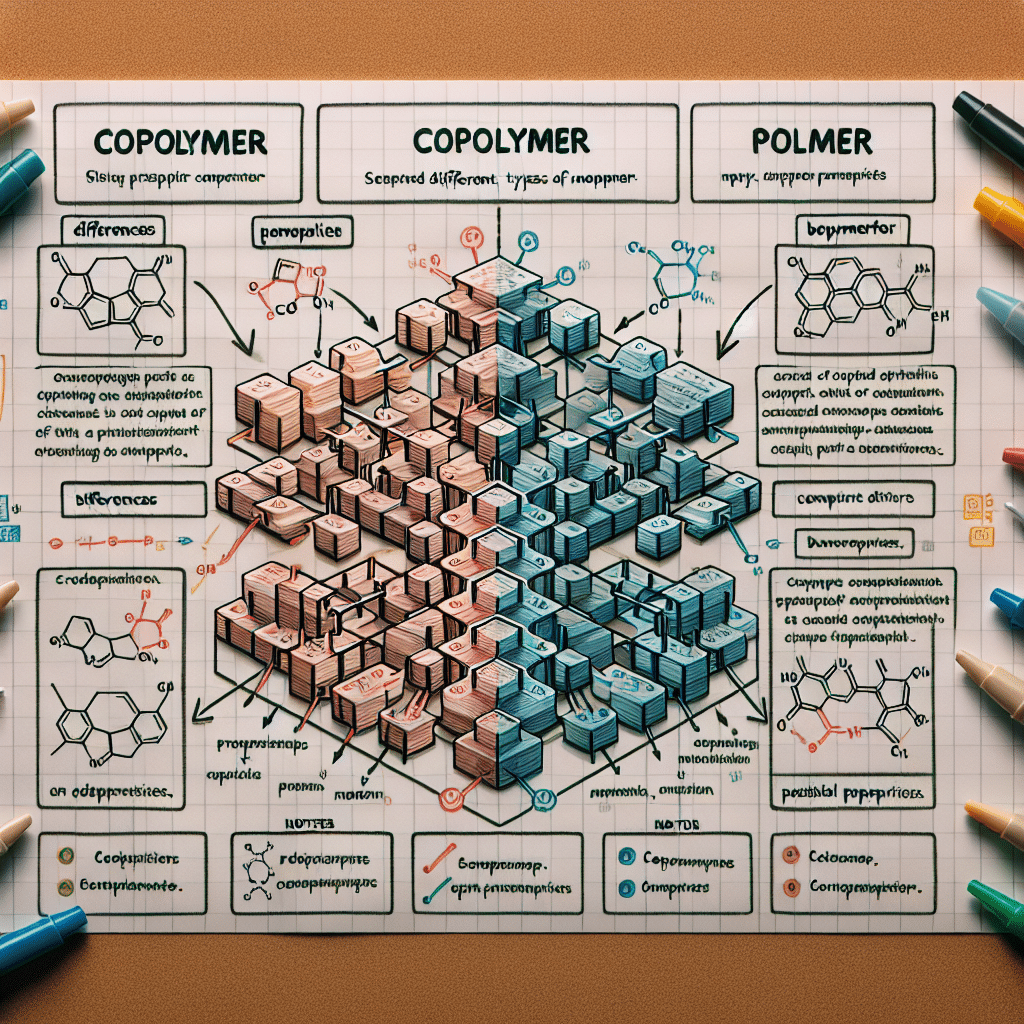
Copolymers are polymers that consist of two or more different types of monomers. The primary distinction between copolymers lies in their structure and composition, which affects their physical and chemical properties. There are three main types of copolymers: random, block, and alternating copolymers. Each type exhibits unique characteristics based on the arrangement of the monomers. This variance provides copolymers with diverse applications across various industries, such as plastics, rubbers, and fibers. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate material for specific uses, from automotive components to medical devices.
Understanding Polymers and Copolymers
To grasp the concept of copolymers, one must first understand what polymers are. Polymers are large molecules composed of repeating structural units called monomers, which are covalently bonded. Natural examples include proteins and cellulose, while synthetic polymers include polyethylene and polystyrene. Copolymers, on the other hand, arise from the polymerization of two or more different types of monomers, leading to materials with varied properties compared to homopolymers made from a single type of monomer.
Types of Copolymers
Copolymers can be categorized into various types based on how their monomers are arranged, each imparting different properties:
- Random Copolymers: The monomers are distributed randomly along the chain, allowing for more flexibility and variability in properties.
- Block Copolymers: These contain large segments or “blocks” of one type of monomer alternating with blocks of another type, leading to distinct physical phases that can improve mechanical properties.
- Alternating Copolymers: These feature a strict alternating sequence of monomers, providing unique chemical reactivity and properties tailored for specific applications.
Key Differences Between Copolymers and Homopolymers
The primary differences between copolymers and homopolymers include:
- Composition: Homopolymers consist of one type of monomer, resulting in uniform properties, while copolymers comprise multiple monomers, leading to a more complex material behavior.
- Properties: Copolymers exhibit improved chemical resistance, toughness, and thermal stability compared to traditional homopolymers. For example, styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), a copolymer, demonstrates better elasticity than rubber made from a single type of monomer.
- Processing: The processing techniques for copolymers can differ substantially. The specific properties associated with each type of copolymer often require tailored processing methods to maximize their utility.
Applications of Copolymers
The versatility of copolymers enables their application across diverse fields:
- Plastics: Copolymers such as acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) are extensively used in the production of tough, lightweight, and glossy finishes.
- Textiles: Many fibers, including nylon and polyester blends, leverage copolymer structures to optimize durability, elasticity, and resistance to wrinkling.
- Adhesives: Copolymers like styrene-ethylene/butylene-styrene (SEBS) are utilized to improve adhesion properties in various applications.
Factors Influencing the Properties of Copolymers
Some of the essential factors that affect the properties of copolymers include:
- Monomer Selection: The choice of monomers and their reactivity determine the final properties of the copolymer.
- Polymerization Method: Techniques such as free radical, anionic, or cationic polymerization lead to different arrangements and qualities in the final product.
- Molecular Weight: The molecular weight of the copolymer influences its mechanical behavior, thermal properties, and overall performance.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their benefits, several challenges exist when working with copolymers:
- Processing Complexity: The varied compositions of copolymers can complicate processing conditions and equipment requirements.
- Cost Factor: The synthesis of copolymers may involve higher production costs compared to homopolymers, due to the need for multiple monomers and specific processing methods.
- Compatibility Issues: In blends or composite materials, ensuring compatibility of different polymers can be challenging and may affect the properties of the end product.
Future of Copolymer Research and Development
As material science evolves, ongoing research focuses on enhancing the properties and developing new copolymers tailored for specific applications. Emerging trends include bio-based copolymers, which address sustainability concerns and promote environmentally-friendly practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the primary benefits of using copolymers?
Copolymers offer enhanced mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and tailored characteristics, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive to healthcare.
2. How do copolymers differ in their physical properties?
The physical properties vary based on the arrangement and type of monomers used, with factors such as flexibility, strength, and thermal resistance being adjustable through copolymer design.
3. Are there environmentally friendly copolymers?
Yes, research is ongoing into bio-based copolymers made from renewable resources, which aim to reduce reliance on petroleum-based materials.
4. Can copolymers be recycled?
Copolymers can be challenging to recycle due to their diverse compositions, but advancements are being made in recycling technologies to recover materials effectively.
5. What industries utilize copolymers extensively?
Copolymers find applications across several industries, including automotive, packaging, construction, and healthcare, owing to their versatile properties.